adbLink is a free, Windows-based utility designed to simplify the process of side-loading Android applications onto devices like the Amazon Fire Stick. While seemingly straightforward in its core function, adbLink operates within a technical landscape requiring a degree of user expertise. This detailed exploration will delve into its functionality, usage, advantages, disadvantages, and alternatives.
Understanding adbLink’s Core Functionality
At its heart, adbLink acts as a bridge, facilitating the transfer of Android Application Packages (APKs) to devices that don’t readily support conventional installation methods. This is particularly useful for devices like the Amazon Fire Stick, which have restrictions on app installations from sources outside the official Amazon Appstore. Instead of requiring users to “root” their device—a complex process involving gaining superuser privileges that can void warranties and compromise security—adbLink provides a comparatively simpler method for side-loading applications. This process bypasses the standard security protocols, allowing users to install applications that might otherwise be unavailable.
The software leverages the Android Debug Bridge (ADB), a command-line tool included in the Android SDK. However, adbLink provides a user-friendly graphical interface, abstracting away the complexities of command-line interactions. This makes the side-loading process accessible to users with limited command-line experience, although a fundamental understanding of IP addresses and networking is still necessary.
Beyond side-loading, adbLink offers additional functionality relevant to managing Android devices, particularly those running media center software like Kodi. One of its key features is the efficient management, backup, and restoration of Kodi data. This capability is invaluable for users who want to maintain their Kodi configurations and settings, ensuring a seamless experience across different devices or after system reinstalls. Essentially, it serves as a crucial link between your Android device and your Windows desktop, streamlining the often-tedious process of data management.
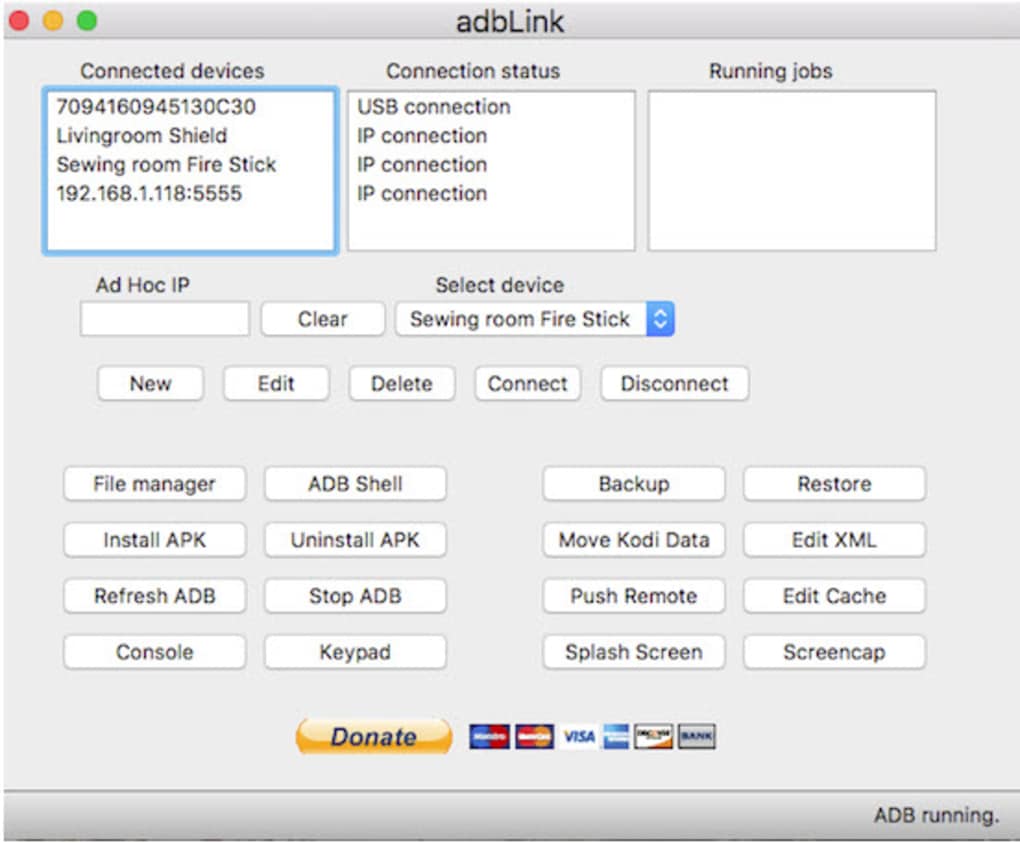
How to Use adbLink on Fire Stick and Other Devices
Setting up and using adbLink requires a careful step-by-step process. While the software itself is designed to simplify side-loading, the preliminary configurations can be challenging for users unfamiliar with networking and Android development concepts.
1. Finding the Fire Stick’s IP Address: Before initiating the side-loading process, you must identify the IP address of your Fire Stick. This is done within the Fire Stick’s settings menu:
- Navigate to Settings on your Fire Stick.
- Select My Fire TV (or equivalent depending on your Fire Stick model).
- Choose About.
- Locate and note down the Network information, specifically the IP address. This address is crucial for adbLink to identify and connect to your Fire Stick.
2. Enabling ADB Debugging: This step is essential for enabling communication between your computer and the Fire Stick. On your Fire Stick:
- Navigate to Settings.
- Select My Fire TV (or equivalent).
- Select Developer options.
- Enable ADB debugging. This may require confirmation and potentially a password.
3. Downloading and Installing adbLink: Download the adbLink executable file from a trusted source. Run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation process.
4. Creating a New Profile: Upon launching adbLink, you’ll likely encounter an empty “Current Device” list. To add your Fire Stick, click the “New” button. You’ll be prompted to provide the following information:
- Description: A brief description to easily identify your device (e.g., “Fire Stick Living Room”).
- IP Address: The IP address you obtained earlier.
- Pull Folder: Specify a local directory where files will be temporarily stored during transfers.
Once this information is entered and saved, adbLink should now recognize your Fire Stick. Leaving other options blank is usually acceptable for initial configuration.
5. Side-Loading Applications: With the connection established, you can now initiate the side-loading process. The exact method may vary slightly depending on the version of adbLink and the specifics of your setup. However, the general process involves selecting the APK file you wish to install and initiating the transfer through adbLink’s interface.
6. Troubleshooting: Problems can arise at any stage of this process. Common issues include incorrect IP addresses, ADB debugging not enabled, firewall restrictions, or network connectivity problems. Thoroughly check each step to ensure accurate configuration. Unfortunately, adbLink doesn’t offer comprehensive documentation or customer support, making troubleshooting more challenging.
Advantages and Disadvantages of adbLink
Advantages:
- Simplified Side-Loading: adbLink significantly simplifies the process of side-loading APKs compared to manual ADB commands. Its graphical interface makes the process more user-friendly.
- Kodi Data Management: The ability to manage, back up, and restore Kodi data is a significant advantage, particularly for users relying on this popular media center software.
- Free of Charge: adbLink is a completely free software solution, eliminating any licensing or subscription costs.
- Android-Windows Bridge: It acts as a convenient bridge between Android devices and Windows computers, facilitating data transfer and management.
Disadvantages:
- Technical Expertise Required: While aiming to simplify the process, adbLink still requires a degree of technical knowledge related to networking, IP addresses, and Android development concepts. Beginners may find the setup process challenging.
- Lack of Customer Support: The absence of readily available customer support or comprehensive documentation can hinder troubleshooting and problem-solving.
- Potential Security Risks: Side-loading applications from untrusted sources poses inherent security risks. It’s crucial to only download APKs from reputable sources to minimize the risk of malware or malicious code.
Alternative Applications and Tools
While adbLink offers a convenient solution, several alternative methods and tools exist for side-loading apps onto Amazon Fire Sticks and other Android devices. These alternatives often offer different features, levels of complexity, and support options:
- Manual ADB commands: Users comfortable with the command line can directly use the ADB tool included in the Android SDK. This offers maximum control but requires a strong understanding of ADB commands and syntax.
- Third-party file managers: Several file management applications for Android offer the ability to install APKs directly from external storage. This method typically requires enabling “Unknown sources” in the Android device’s settings.
- Other side-loading tools: Several other graphical tools similar to adbLink exist, each with its own features and user interfaces. Researching these alternatives may reveal options with better documentation or support.
Conclusion
adbLink presents a valuable tool for users seeking to bypass restrictions on app installations on devices like the Amazon Fire Stick. Its user-friendly graphical interface simplifies the process relative to manual ADB commands. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations, including the technical expertise required for setup and the absence of official support. Users should carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages against alternative methods before adopting adbLink as their preferred side-loading solution. Always prioritize security by downloading APKs only from verified and trustworthy sources. Ultimately, the suitability of adbLink depends on the user’s technical skills and comfort level with potentially complex configurations.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Version: “3.5”
- Latest update: “July 20, 2021”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 7”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “8.9K”
















