BitTornado, a now-defunct BitTorrent client, holds a significant place in the history of peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing. While overshadowed by later, more popular clients like uTorrent and BitTorrent, BitTornado played a crucial role in the evolution of BitTorrent technology and offered a unique set of features for its time. This article delves into the history, features, and legacy of BitTornado, exploring its impact on the P2P landscape.
BitTornado’s Genesis and Development
BitTornado emerged as a successor to Shad0w’s Experimental Client, both projects spearheaded by the same developer. Building upon the foundational BitTorrent protocol, BitTornado aimed to enhance the user experience and functionality beyond the original client. This involved incorporating several key improvements that addressed limitations and added user-friendly features. The project’s open-source nature, released under the GPL license, fostered community involvement and allowed for further development and modification. While precise release dates are difficult to pin down from available online resources, its development spanned several years, with updates introducing new capabilities and addressing bugs. The last publicly available version, 0.3.18, was released around May 1, 2007, although later updates may have existed privately or within specific community builds.
One of the significant aspects of BitTornado’s development was its active community. This community played a pivotal role in testing, identifying bugs, and suggesting enhancements. This collaborative approach is indicative of the open-source ethos that underscored the project. However, the lack of sustained updates and the rise of more feature-rich and actively maintained clients ultimately led to its decline in popularity.
Key Features and Functionality
BitTornado offered a robust set of features for a BitTorrent client of its era. Unlike many contemporary options, its focus lay on speed and efficiency, while maintaining a relatively straightforward user interface. Key features included:
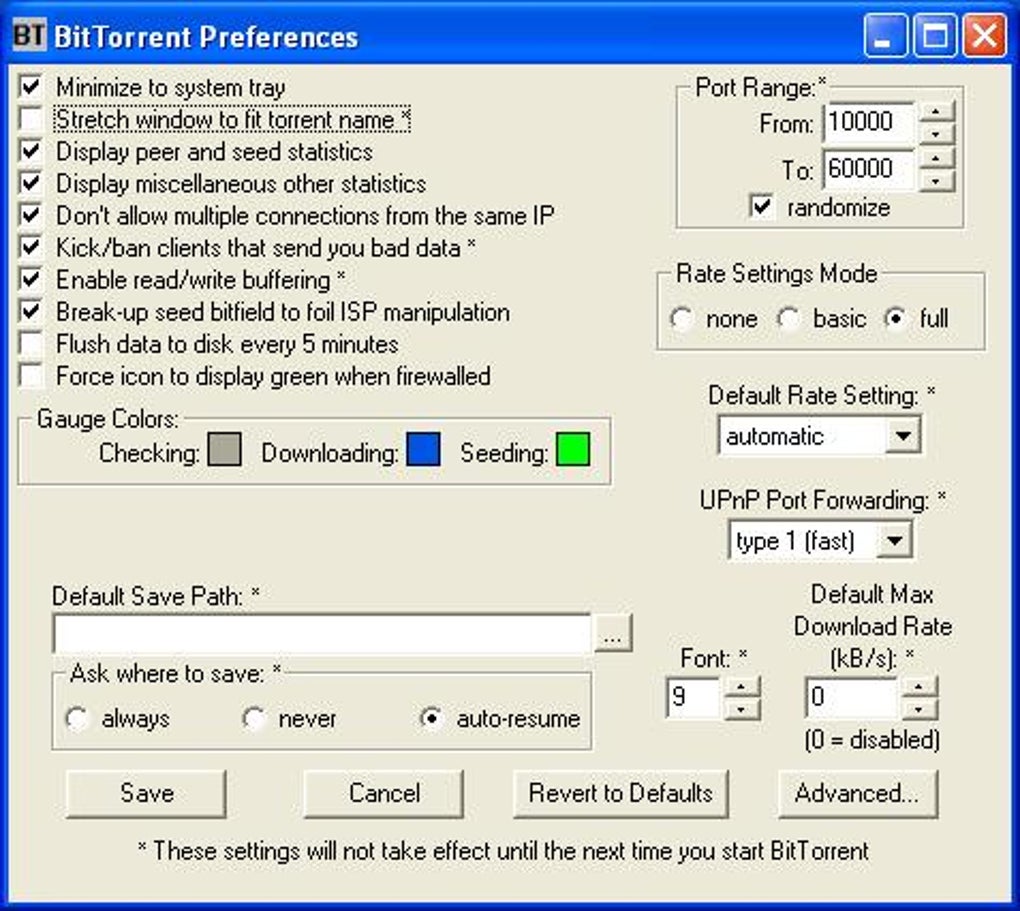
- Upload/Download Speed Limitation: Users could customize their upload and download speeds, allowing them to manage bandwidth usage and prioritize other internet activities. This was crucial for users with limited bandwidth connections, common at the time.
- Prioritized Downloading: When downloading multiple files simultaneously, BitTornado allowed users to prioritize specific files, ensuring that important downloads completed faster. This feature was essential for managing large torrent downloads containing many files.
- Detailed Connection Information: The client provided detailed information about the connections to other peers in a torrent swarm. This provided users with insight into their download process and allowed for troubleshooting network connectivity issues.
- UPnP Port Forwarding: BitTornado supported Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) port forwarding. This automated the process of configuring routers to forward the necessary ports for optimal BitTorrent performance. This simplified the setup process considerably for less technically adept users, removing a significant barrier to entry for many.
- Super Seeding and Web Seeding: BitTornado incorporated super seeding and web seeding capabilities. Super seeding allowed users with complete copies of a torrent to prioritize uploads, increasing download speeds for others. Web seeding enabled downloading directly from web servers in addition to peers, providing an additional source of data and bolstering download speeds, particularly in situations with limited peer availability. This significantly enhanced the overall download experience compared to solely peer-to-peer transfer.
- Encryption: While specific details are scarce regarding the implementation, BitTornado incorporated encryption features in later versions to enhance security and privacy during file transfers. This was a crucial addition considering the increasing scrutiny of P2P activities. This aimed to protect user data from potential monitoring and interception.
These features, while not revolutionary in hindsight, represented a notable improvement over the original BitTorrent client, making BitTornado a more user-friendly and efficient alternative. The attention to detail and the integration of these features showcased the developers’ dedication to creating a reliable and robust P2P solution.
BitTornado’s Place in the P2P Ecosystem
BitTornado existed in a highly competitive market. The BitTorrent protocol’s popularity spawned numerous clients, each striving to differentiate itself through features, performance, and user experience. While BitTornado never achieved the widespread adoption of later clients like uTorrent, it nonetheless contributed significantly to the overall advancement of BitTorrent technology and the P2P ecosystem.
Its open-source nature fostered a community of users and developers, contributing to the improvement and evolution of the software. The features implemented in BitTornado, particularly the improved bandwidth management, prioritized downloading, and enhanced connection information, became standard features in many subsequent BitTorrent clients. This showcases the enduring influence of BitTornado’s development on the overall landscape of P2P file sharing software.
The focus on speed and efficiency, while not the sole differentiator in a crowded market, became a critical element in the success of many later clients. BitTornado’s contributions directly or indirectly shaped the user expectations and design choices made by other developers in the subsequent years. Its relatively simple interface, while lacking the advanced features of some later clients, provided a streamlined user experience that was appealing to many.
Decline and Legacy
Despite its initial success and noteworthy features, BitTornado eventually declined in popularity. Several factors contributed to its eventual obsolescence.
- Lack of Active Development: The cessation of active development and updates left BitTornado vulnerable to security vulnerabilities and incompatible with newer operating systems. As the P2P landscape evolved, its lack of updates meant it failed to keep pace with improvements in the BitTorrent protocol and emerging security threats.
- Competition from More Mature Clients: The emergence of clients like uTorrent and BitTorrent, which offered more features, regular updates, and more user-friendly interfaces, outcompeted BitTornado. These clients capitalized on the market demand for a more feature-rich and actively supported BitTorrent client.
- Changing Technological Landscape: Changes in internet infrastructure, increasing bandwidth availability, and the rise of cloud-based services impacted the relevance of P2P file sharing applications. The changing landscape made previously critical features less crucial, diminishing the competitive advantage of BitTornado.
Despite its eventual decline, BitTornado’s legacy remains significant. It served as a stepping stone in the development of BitTorrent clients, contributing to the functionality and user experience of subsequent software. Its open-source nature further enabled community contribution and the ongoing evolution of P2P technology. Although no longer actively supported, its contributions to the evolution of the BitTorrent ecosystem are undeniable.
Conclusion
BitTornado represents a significant chapter in the history of P2P file sharing. While it may not be remembered with the same prominence as some of its more successful contemporaries, its impact on the development of BitTorrent technology and the user experience of P2P applications is undeniable. Its features, rooted in efficiency and user control, were absorbed and enhanced in successive generations of clients. BitTornado serves as a reminder of the iterative nature of software development and the essential role of community contributions in the ongoing evolution of technology. While it may be gone, its influence continues to shape the landscape of P2P file sharing even today.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Version: “0.3.18”
- Latest update: “January 10, 2022”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 98 SE”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “38.6K”
- Size: “4.32 MB”
















