The world of remote-controlled (RC) cars has undergone a significant transformation with the advent of Bluetooth technology. This innovative connectivity allows for a seamless integration of smartphones and other smart devices, offering users a level of control and customization previously unimaginable. This guide explores the exciting possibilities of Bluetooth RC cars, focusing on the popular Bluetooth RC Car app and its functionalities, while also delving into the technical aspects, modifications needed, and potential alternatives.
Understanding the Bluetooth RC Car App
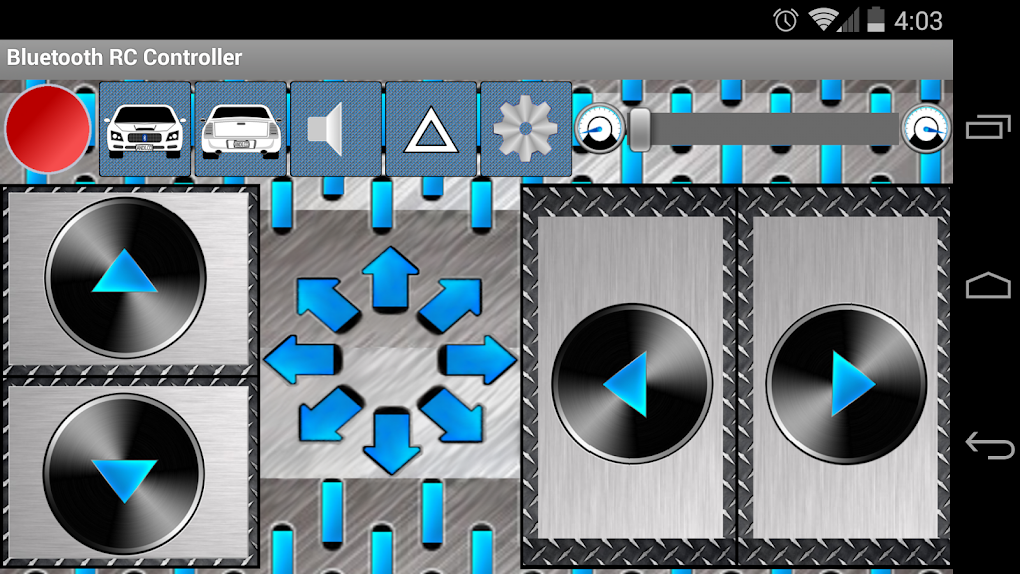
The Bluetooth RC Car app, developed by Andi.Co, provides a user-friendly interface for controlling modified RC cars via a Bluetooth connection. This free Android application transforms your smartphone into a versatile remote control, offering a range of control options and features to enhance the RC driving experience. While readily accessible and easy to use, it’s crucial to understand its limitations and the modifications required to utilize it effectively. The app is not designed to work with commercially available, unmodified RC cars; it requires specific hardware and software modifications to establish a proper connection and control functionality.
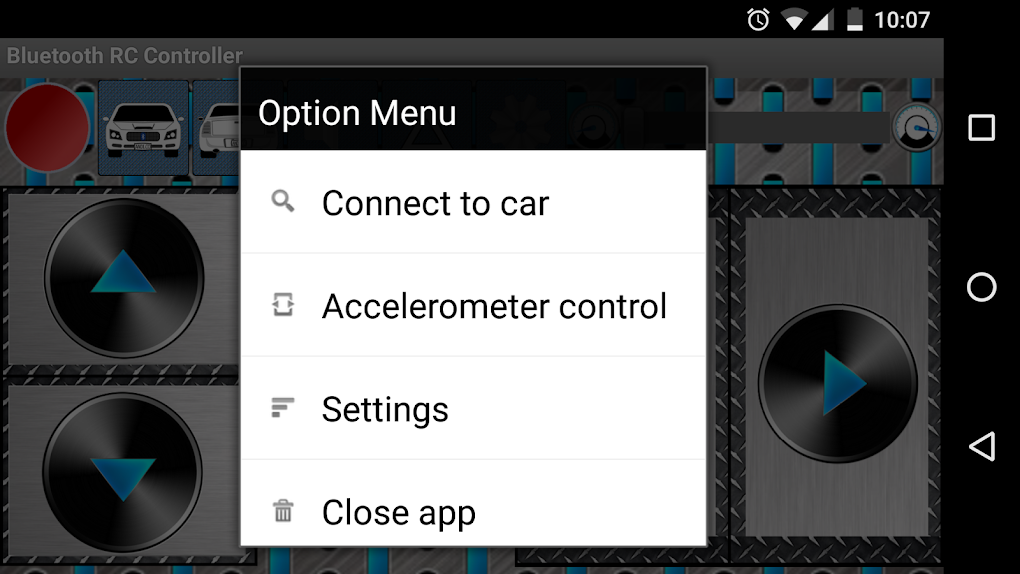
The application’s simplicity is one of its key strengths. The primary interface provides intuitive controls, allowing users to easily navigate and manipulate the RC car. These controls are primarily divided into two categories: virtual buttons and accelerometer control. The virtual buttons provide direct directional commands (forward, reverse, left, right), offering a precise method of maneuvering the car. The accelerometer option, on the other hand, allows for more dynamic control, with the car’s direction responding directly to the tilting of the smartphone. This provides a more immersive and interactive driving experience, mirroring the physical movements of the user.
Furthermore, the app integrates a speed slider, allowing for precise speed adjustments. This feature is particularly useful for navigating challenging terrains or performing intricate maneuvers. The speed control’s functionality depends on the capabilities of the RC car’s control circuit. Not all modified RC cars will have this feature supported, and it’s important to ensure compatibility before expecting this level of precision.
Beyond basic directional and speed controls, the Bluetooth RC Car app also provides the ability to control the car’s lighting system. The app allows users to switch the car’s headlights and taillights on and off, providing improved visibility in low-light conditions. This feature adds a practical element to the driving experience, particularly when operating the car in dimly lit environments or at night.
Necessary Modifications for Compatibility
As previously emphasized, the Bluetooth RC Car app’s functionality relies heavily on the modification of the RC car itself. It will not work with standard, off-the-shelf RC cars. The app requires a specific Bluetooth-equipped microcontroller to be integrated into the car’s existing circuitry. This microcontroller acts as the intermediary between the app and the car’s motor and control systems. This modification is a critical step and is not a simple task, requiring a degree of technical expertise and understanding of electronics.
The process typically involves replacing or augmenting the existing RC car’s control board with a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or similar platform. This microcontroller is then programmed to receive instructions from the Bluetooth RC Car app via a Bluetooth module. The program’s code must be meticulously written to interpret the commands received from the app and translate them into appropriate signals to control the car’s motor, steering, and lighting systems. This necessitates a good understanding of programming languages like C++ or similar languages commonly used for microcontroller programming.
The process involves several key steps:
-
Selecting a suitable microcontroller: Choosing the right microcontroller is crucial. It needs to have sufficient processing power and memory to handle the application’s commands and control the car effectively. Popular choices include various Arduino boards or similar microcontrollers readily available online.
-
Acquiring necessary components: Along with the microcontroller, users will need a Bluetooth module capable of establishing communication with smartphones. Other components will also be required, such as motor drivers and wiring for connections to the RC car’s various components.
-
Programming the microcontroller: The selected microcontroller must be programmed to receive and interpret commands from the Bluetooth RC Car app. This process often involves writing custom code to map the app’s inputs (forward, reverse, left, right, speed, lights) to the appropriate actions on the car.
-
Integrating the microcontroller into the RC car: This step involves carefully integrating the microcontroller and its associated components into the RC car’s chassis. This requires careful soldering and wiring to ensure proper functionality and to avoid short circuits.
-
Testing and calibration: After installation and wiring, thorough testing is essential to ensure that the modified RC car functions correctly. This may involve calibrating the controls to optimize the response of the car to the app’s commands.
The specific details and steps involved in the modification process will vary depending on the type of RC car used, the chosen microcontroller, and the user’s comfort level with electronics and programming. Detailed guides and resources are readily available online for those who wish to undertake this modification.
App Features and User Interface
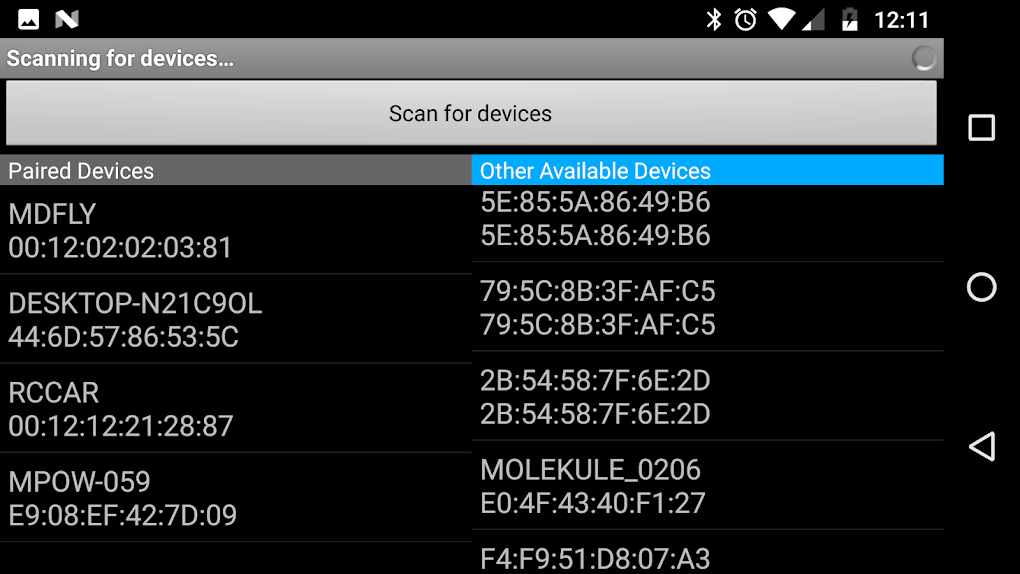
The Bluetooth RC Car app boasts a relatively simple yet effective user interface. The main screen typically displays the control buttons or accelerometer input area, alongside a speed slider. Visual cues, such as flashing lights or direction indicators, are provided to offer visual feedback on the car’s status and direction of travel. A clear connection indicator also helps the user understand whether the app is successfully communicating with the modified RC car.
The use of virtual buttons is straightforward, offering clear directional controls that are readily apparent to the user. The accelerometer-based control offers a more dynamic experience, using the phone’s orientation to directly control the RC car’s movement. This control scheme can take some practice to master, but it ultimately offers a more immersive feel.
The speed slider, when supported by the car’s control system, provides a level of control that’s hard to achieve with simple on/off controls. This allows users to adjust the speed of their car precisely and adapt their driving style according to the terrain or the situation.
The inclusion of headlight and taillight control demonstrates a thoughtful consideration of functionality. While seemingly a small feature, it significantly enhances the usability of the app, especially in darker environments.
Alternative Apps and Solutions
While the Bluetooth RC Car app offers a viable solution for controlling modified RC cars, other alternatives exist in the market. These alternatives may offer different functionalities, control schemes, or levels of customization. Some might offer advanced features, such as programmable macros or pre-set driving profiles, while others might provide compatibility with a wider range of microcontrollers and RC car models.
One notable consideration is the use of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology. BLE offers lower power consumption and better range compared to standard Bluetooth, making it particularly attractive for RC car applications. Apps that support BLE connectivity might offer improved performance and battery life, but they also necessitate the use of BLE-compatible microcontrollers and modules.
The choice of alternative app or solution often depends on the specific requirements and preferences of the user. Factors to consider include the type of RC car being used, the level of technical expertise, and the desired level of control and customization. Researching and comparing different applications available on app stores or exploring open-source projects is recommended to find a solution that best suits the user’s needs.
Conclusion
Bluetooth RC cars offer a modern and engaging approach to remote-controlled vehicles. The Bluetooth RC Car app, though requiring modifications to the RC car itself, provides a user-friendly platform for controlling modified RC cars. Its intuitive interface, coupled with various control options and the inclusion of lighting controls, enhances the overall user experience. Understanding the limitations and modifications required is crucial before using the app. For those willing to undertake the modification process, the app presents an exciting and innovative way to control their RC cars. Exploring alternative applications and BLE technology can further expand the options and capabilities available to RC enthusiasts, creating a truly personalized and customizable driving experience.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Version: “2.1”
- Latest update: “April 29, 2024”
- Platform: “Android”
- OS: “Android 9.0”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “116.4K”
- Size: “4.36 MB”
- Download Options: “APK, Google Play”
- Filename: “braulio.calle.bluetoothRCcontroller.apk”