Facebook Password Dump was a command-line utility designed to recover Facebook login credentials stored within various web browsers installed on a Windows PC. While no longer available for download, understanding its functionality and the security implications surrounding such tools remains crucial. This article explores the capabilities, limitations, and inherent risks associated with password-dumping software like Facebook Password Dump.
Functionality and Supported Browsers
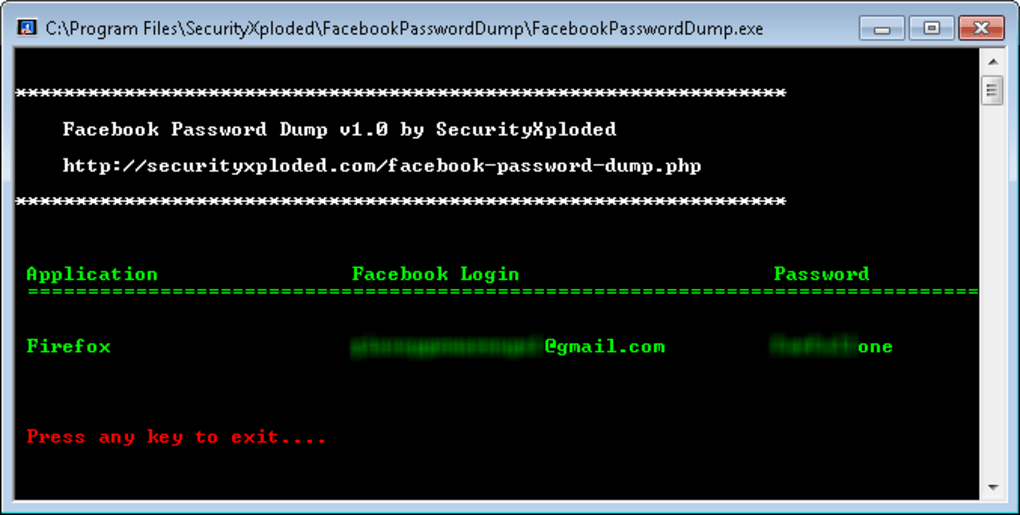
Facebook Password Dump operated by analyzing the user’s browser data to extract stored Facebook login information – specifically, the username and password. The program’s strength lay in its broad compatibility with popular browsers prevalent at the time of its release. It claimed support for a wide range of browsers, including but not limited to:
- Firefox
- Chrome
- Internet Explorer (versions 6-10)
- Opera
- Safari
- Flock
- SeaMonkey
- Comodo Dragon
- Paltalk Messenger
- Miranda Messenger
- CoolNovo
This extensive browser support implied that users who had inadvertently saved their Facebook login details within any of these applications were potentially vulnerable to having their credentials exposed by this tool. The program’s ability to access this information underscored the significance of practicing good password hygiene and regularly reviewing browser security settings.
The program’s design was entirely command-line based, meaning it lacked a graphical user interface (GUI). This aspect, while potentially deterring less technically proficient users, simplified the core function: retrieving stored credentials from supported browsers and displaying them on the command prompt. The absence of a GUI streamlined the program’s execution and minimized resource consumption, a feature appreciated in less powerful computing environments of its time.
Limitations and Security Concerns
Despite its purported functionality, Facebook Password Dump possessed several notable limitations. One significant drawback was the absence of any data export or saving capabilities. The retrieved credentials were only displayed on the command prompt; users could not save them to a file for later use. This constraint made the program’s usefulness largely confined to immediate credential retrieval. Users were required to manually record the displayed credentials, introducing potential errors and adding inconvenience to the process.
More importantly, the tool’s existence highlights the security vulnerabilities inherent in how some browsers handle password storage. Browsers designed to offer convenience often store passwords in a manner that, while convenient, can be exploited by malicious software. Facebook Password Dump, however inadvertently, served as a testament to the need for enhanced security measures within browsers and the importance of regularly updating software and using strong, unique passwords for each online account.
Furthermore, the original download links for Facebook Password Dump are no longer functional, raising questions about the tool’s long-term maintenance and the potential for outdated security vulnerabilities. The fact that the software is no longer available for download suggests that either the developer ceased its support or that the program’s functionality was rendered obsolete or insecure by updated browser security protocols. The unavailability of the program is a positive step, as its continued existence would have presented a consistent security risk.
Downloading and using applications like Facebook Password Dump presents inherent risks beyond the ethical concerns of accessing another person’s account. Older, unsupported software may contain malicious code or vulnerabilities that expose a user’s system to further attacks. Malware could be introduced through a corrupted download, giving malicious actors access to sensitive personal information beyond Facebook credentials.
The warning “The file might contain threats” associated with the application further underscores these security risks. This warning suggests that antivirus software detected malicious elements within the program or flagged it due to its potential for misuse. Such warnings should never be ignored; any software raising such flags should be avoided to protect the user’s system and personal data.
Ethical Considerations
The ethical ramifications of using software like Facebook Password Dump are profound. Accessing someone’s Facebook account without their explicit permission is a violation of privacy and potentially illegal. The program’s purpose, even if intended for personal use in recovering a forgotten password, opens the door for potential misuse. Unauthorized access to an individual’s Facebook account can lead to significant harm, including:
- Identity theft: Malicious actors could use the retrieved credentials to access other online accounts linked to the Facebook profile.
- Financial fraud: Access to financial information shared on Facebook could facilitate fraudulent transactions.
- Reputation damage: Unauthorized posts or actions on the compromised account can severely damage the individual’s reputation.
- Social engineering: The stolen credentials could be leveraged in social engineering attacks against friends and family.
Therefore, using Facebook Password Dump, or similar tools, should be strongly discouraged. Legitimate methods for recovering forgotten Facebook passwords exist, and these methods should always be prioritized. Relying on potentially malicious software to recover a password poses significant risks and has serious ethical implications.
Alternatives and Best Practices
Instead of resorting to potentially harmful applications like Facebook Password Dump, users should explore the officially supported methods offered by Facebook for password recovery. Facebook provides a streamlined process for users to recover their account access through various methods, including email verification and mobile device verification. These methods ensure account security while respecting the user’s privacy and adhering to established security protocols.
Furthermore, practicing robust password management is crucial to prevent the need for password recovery tools altogether. Implementing the following best practices can significantly reduce the risk of compromised accounts:
- Use strong, unique passwords: Employ passwords that are long, complex, and unique to each online account. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or pet names.
- Use a password manager: A password manager stores and manages your passwords securely, eliminating the need to remember multiple complex passwords.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security using 2FA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized account access even if a password is compromised.
- Regularly update software: Keeping your operating system, browsers, and other software up-to-date protects against known vulnerabilities that malicious actors could exploit.
- Be cautious of phishing attempts: Be wary of suspicious emails or messages that may attempt to trick you into revealing your login credentials.
By adhering to these security best practices, users can significantly reduce their vulnerability to password-related attacks and avoid the need for potentially risky tools like Facebook Password Dump. The prioritization of official password recovery methods and the implementation of sound security practices are paramount in maintaining online safety and protecting personal information.
















