Data loss can strike at any time, leaving you with corrupted files that refuse to open. Whether it’s a sudden power outage, a malicious virus attack, or a simple file system error, the frustration of inaccessible data is a common problem. File repair software offers a lifeline, providing a means to recover precious information from damaged files. This guide dives deep into the world of file repair, exploring its capabilities, limitations, and alternatives, specifically focusing on File Repair software for Windows.
Understanding File Corruption and its Causes
File corruption occurs when the structural integrity of a file is compromised, rendering it unreadable or unusable. This disruption can manifest in various ways, from minor glitches to complete data loss. Understanding the root causes of corruption is crucial for effective prevention and recovery. Several factors can contribute to file corruption:
-
Software Errors: Bugs or glitches within the application used to create or edit the file can lead to inconsistencies in its data structure. A sudden program crash during file saving, for example, can leave a file in a partially written state.
-
Hardware Failures: Malfunctioning hard drives, SSDs, or other storage devices can introduce errors that corrupt stored data. Bad sectors on a hard drive, for example, can damage parts of files, resulting in unreadable content.
-
Virus Attacks: Malware can directly overwrite or corrupt files, rendering them unusable. Viruses designed to destroy data or encrypt it for ransom can cause significant damage. Antivirus software plays a critical role in preventing such attacks.
-
Power Failures: Interruptions in power supply can abruptly halt file operations, leaving files incomplete or inconsistent, similar to software crashes.
-
Network Interruptions: Network-related issues can disrupt the transmission and storage of files, particularly when transferring large files across networks. Corruption may occur if the transfer is interrupted midway.
-
Incomplete Downloads: Downloading files from unreliable sources can lead to incomplete or corrupted files. The missing portions make the file unusable, leading to errors upon attempting to open the file.
-
File System Errors: Issues with the file system itself (like NTFS or FAT32) can cause files to become corrupted. Errors in file allocation tables or directory structures can corrupt file pointers, leaving data inaccessible.
-
Physical Damage: Physical damage to storage media, such as scratches or impacts to a USB drive or CD, can directly damage the underlying data, making recovery challenging.
The impact of file corruption can range from minor inconveniences to significant data loss. A slightly corrupted image might exhibit minor visual artifacts, whereas a severely corrupted database could lead to the complete loss of essential information.
File Repair Software: A Solution to Data Recovery
File repair software provides a means to recover data from corrupted files. These specialized programs analyze the structure of damaged files, identify the corrupted sections, and attempt to reconstruct the data. Different types of files require different techniques for repair.
File Repair software often employs techniques that involve:
-
Data Extraction: This involves recovering usable portions of the file that are still intact. Even if the complete file structure is broken, some parts of the data might still be retrievable.
-
Structure Reconstruction: This tries to recreate the internal structure of the file based on what can be salvaged and known file formats. The software uses algorithms to predict and recreate missing parts of the file.
-
Data Validation: During the repair process, the software validates the recovered data to ensure its integrity and accuracy.
-
Error Correction: The software identifies and corrects errors in the file’s data based on file format specifications and error-correcting codes.
Not all file repairs are successful. The success rate often depends on the severity of the corruption, the type of file, and the capabilities of the software. Heavily corrupted files are more challenging to repair.
File Repair for Windows: Features and Functionality
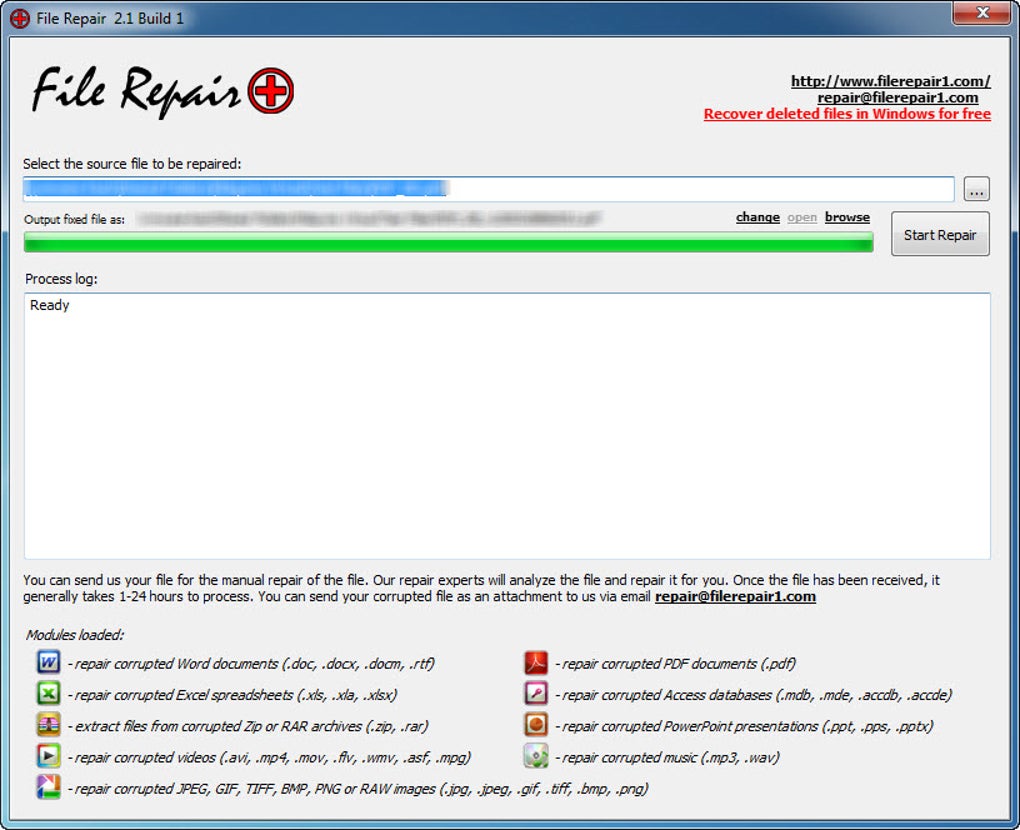
File Repair, as the name suggests, is a Windows-based utility designed to mend damaged files. It boasts a straightforward interface, making it user-friendly even for those without advanced technical skills. Its primary functionality includes:
-
Support for Multiple File Types: It aims to recover various file types, including Microsoft Office documents (Word, Excel, PowerPoint), Access databases, compressed archives (ZIP, RAR), images, PDFs, videos, and audio files. The breadth of supported formats is a key advantage, making it a versatile tool.
-
File Scanning and Analysis: The software scans the selected file for damage or errors and determines the extent of the corruption. This analysis informs the repair process, allowing the software to focus on the most recoverable portions.
-
Data Recovery and Reconstruction: Based on the scanning results, the software extracts recoverable data and attempts to reconstruct the original file structure. The output is a new file containing as much of the recovered data as possible.
-
Simple User Interface: The software’s interface prioritizes ease of use. Even inexperienced users will find it relatively easy to navigate and use.
-
Freeware: File Repair is readily available as freeware, offering accessibility to a wide range of users. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for users who only occasionally encounter file corruption issues.
Limitations and Alternatives to File Repair
While File Repair offers a valuable service, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations:
-
Interface Simplicity: The simple interface, while beneficial for usability, may lack advanced options that are present in more professional-grade software. Some users may find this restrictive.
-
Repair Time: Scanning and repairing files can be time-consuming, especially for larger files with extensive corruption.
-
Incomplete Repairs: Not all files are repairable. The software might not be able to completely recover all data from severely damaged files.
-
Limited File Type Support: Though it claims broad support, the extent of recovery might vary significantly depending on the file type and the nature of the corruption.
Considering these limitations, exploring alternatives to File Repair is advisable:
-
RS File Repair: Offers specific support for image and video repair with a more advanced interface. However, it’s a trial version.
-
JPEG Repair PRO: Specializes in repairing JPEG images and is a trial version.
-
Word Repair: Focuses solely on Microsoft Word documents and is freely available.
-
Hetman File Repair: This option offers a more comprehensive approach to file recovery but is a trial version with limitations for the free usage.
-
Recuva: A robust data recovery tool that can recover deleted or lost files, including some corrupted files. Recuva is free to use.
These alternatives offer diverse functionalities and levels of advanced features. Choosing the right tool depends on the specific files to be repaired and the user’s technical expertise. Some tools excel in specific file types, while others are more general-purpose.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right File Repair Solution
File corruption is a frustrating yet common issue that can cause significant data loss. While File Repair provides a readily accessible and free option for dealing with such problems, its limitations might necessitate exploring other alternatives depending on the file type, the extent of corruption, and the user’s needs. Understanding the causes of file corruption, and the strengths and weaknesses of various file repair tools, is crucial for selecting the right approach to recover valuable data. Remember that prevention is always better than cure: regular backups and reliable antivirus software are essential safeguards against data loss.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Version: “2.1.2”
- Latest update: “October 9, 2011”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 8”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “600.4K”
- Size: “1.07 MB”
















