In the ever-evolving landscape of digital communication, certain tools emerge, capture widespread attention, and fundamentally shift how we connect. Google Voice and Video Chat was one such innovation, marking a significant milestone in Google’s journey to integrate seamless voice and video capabilities directly into its pervasive Gmail platform. While the original iteration described here has since evolved into more modern solutions like Google Hangouts, and subsequently Google Chat and Google Meet, understanding its initial impact and design provides crucial context for the communication tools we rely on today.
At its core, Google Voice and Video Chat was a plug-in designed to empower Gmail users with the ability to conduct real-time video conferences and voice calls with their contacts. It was a natural progression from Google Talk, Google’s minimalist instant messaging client, transforming it from a text-centric application into a comprehensive multimedia communication hub. This shift was not merely incremental; it represented a bold step towards a future where geographical distances would no longer be a barrier to face-to-face interaction, bringing families, friends, and colleagues closer through the ubiquity of the internet.
The Dawn of Seamless Communication: Google Voice and Video Chat’s Legacy
Before the advent of widespread high-speed internet and ubiquitous video conferencing platforms, connecting visually with someone across the globe was often cumbersome, requiring specialized software, dedicated hardware, and complex configurations. Google Voice and Video Chat emerged into this environment, offering a refreshingly simple and integrated solution that resonated deeply with users already familiar with the Gmail ecosystem.
From Google Talk to a Multimedia Powerhouse
Google Talk, launched in 2005, initially offered a straightforward instant messaging experience, allowing users to exchange text messages with their Gmail contacts. It was praised for its simplicity, speed, and integration with the Gmail interface, which was revolutionary for its time. However, as internet speeds improved and webcams became more common, the demand for richer communication methods grew exponentially. Recognizing this, Google embarked on an ambitious journey to enhance Google Talk’s capabilities, culminating in the release of the Voice and Video Chat plug-in.
This transformation was more than just adding a new feature; it was about reimagining how people could interact within an existing, highly popular platform. By building upon the established foundation of Google Talk, Google ensured a degree of familiarity and ease of adoption. Users didn’t have to learn an entirely new application; they simply enhanced their existing Gmail experience. This strategic integration was key to its rapid acceptance and laid the groundwork for future Google communication products. The plug-in essentially breathed new life into Google Talk, elevating it from a simple chat application to a true communications suite, capable of handling voice and video with impressive fidelity for its era. It represented Google’s vision of a unified communication experience, where various modes of interaction – text, voice, and video – were seamlessly intertwined.
Integrating Voice and Video into Gmail
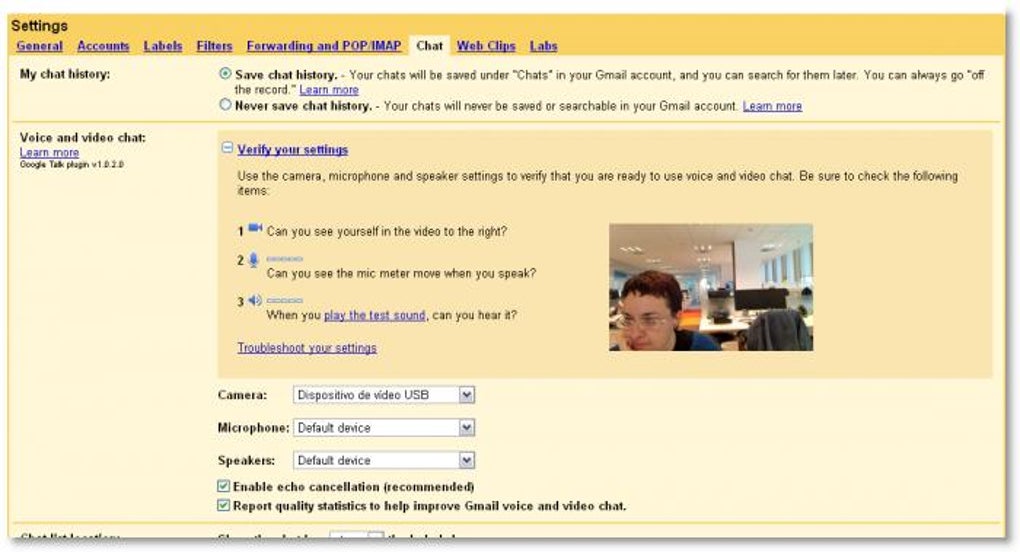
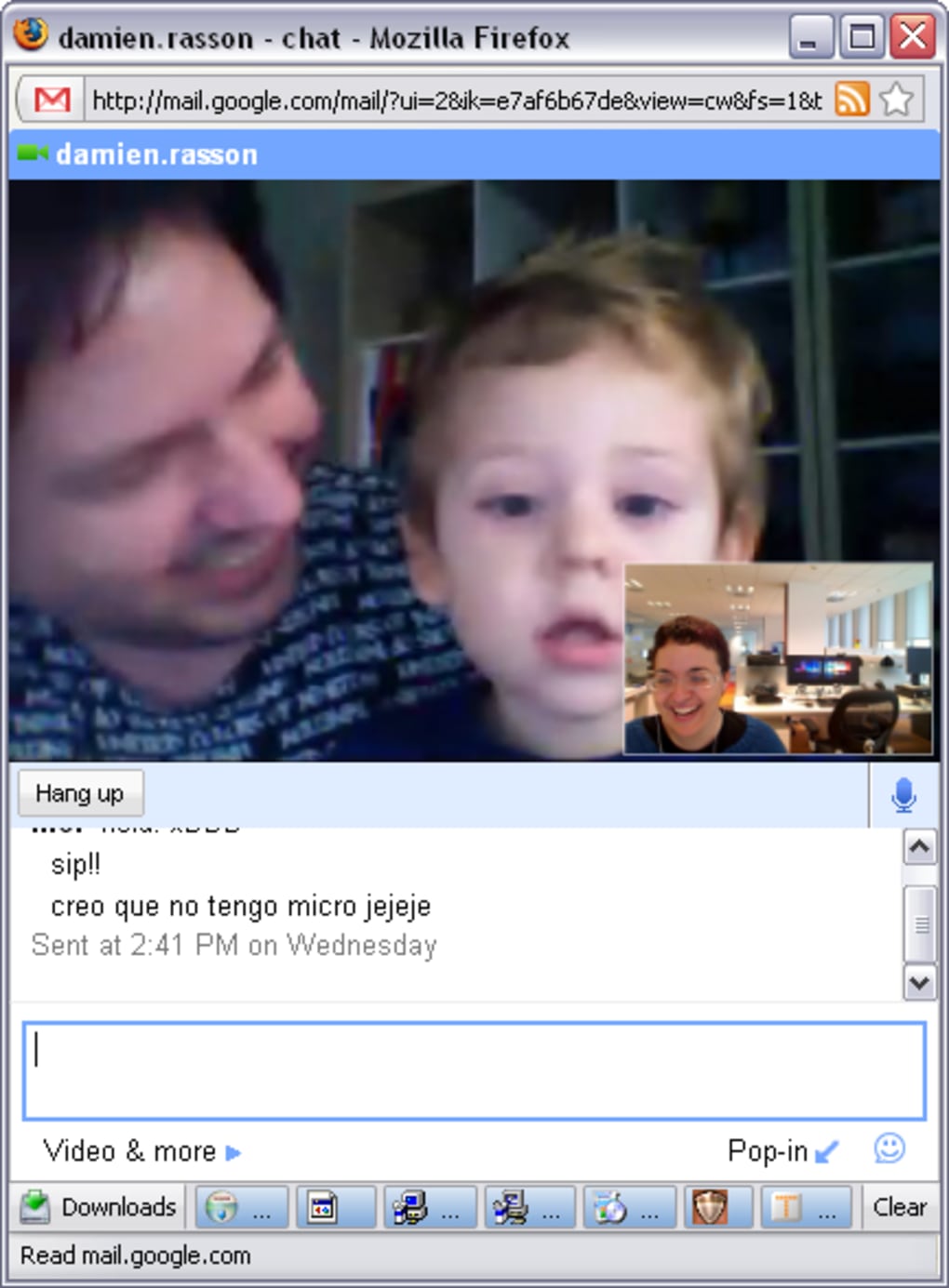
The most remarkable aspect of Google Voice and Video Chat was its seamless integration directly into the Gmail interface. Unlike other video calling applications that required users to open separate programs, Google’s solution allowed users to initiate and participate in video conferences right alongside their email and text chats. This meant less friction, fewer steps, and a more intuitive user experience. When a contact was available, a simple click could transform a text conversation into a live video call, fostering a sense of immediate connection previously difficult to achieve.
When a video call was active, a dedicated video window would appear, typically on the right side of the Gmail interface. While this embedded window had a fixed position initially, preventing users from moving it freely, Google wisely included an option to “pop out” the video feed. This crucial feature allowed users to detach the video window from the main browser interface and place it anywhere on their desktop, offering flexibility for multitasking or simply arranging their screen layout to their preference. This attention to user convenience, even in its early stages, highlighted Google’s commitment to creating practical and user-friendly communication tools. The ability to pop out the window was particularly appreciated by users who needed to reference documents or other applications while on a call, enhancing productivity and making the video chat experience more adaptable to different workflows.
A Closer Look at Features and Performance
The success of any communication tool hinges not just on its availability but on its performance and ease of use. Google Voice and Video Chat excelled in these areas, offering a quality experience that set a high standard for browser-based communication at the time.
Unparalleled Quality and User Experience
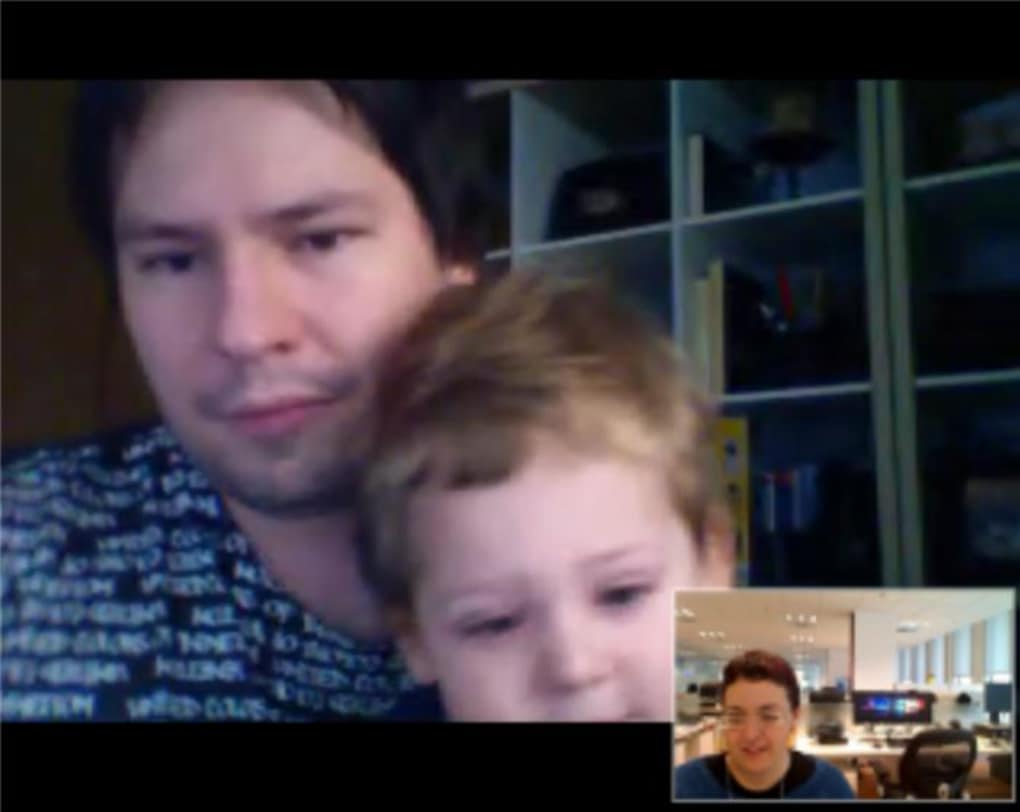
One of the most frequently lauded aspects of Google Voice and Video Chat was its exceptional audio and video quality. Users consistently reported an “astounding quality” in both image and sound. Video streaming was remarkably smooth, minimizing lag and pixelation, which was a common issue with other platforms of the era. Sound was described as “crisp and clear,” ensuring that conversations were easy to follow and misunderstandings due to poor audio were rare. This high fidelity was a significant differentiator, contributing greatly to a positive and immersive communication experience. For many, it provided a glimpse into the potential of what reliable, high-quality video communication could offer.
Crucially, this impressive performance did not come at the cost of complicated setup procedures. Google Voice and Video Chat was designed with user accessibility in mind, requiring “no complicated configuration settings.” The installation process was straightforward, often described as taking “two minutes” to get up and running. This “plug-and-play” simplicity was a major advantage, eliminating the technical hurdles that often deterred less tech-savvy users from adopting video communication. The low barrier to entry meant that more people could connect visually, bridging digital divides and making remote interaction a reality for a broader audience. The intuitive design ensured that users could focus on their conversations rather than grappling with software settings.
Setup, Requirements, and Minor Limitations
Despite its advanced capabilities, Google Voice and Video Chat maintained minimal requirements, making it accessible to a vast user base. As a Google Talk plug-in, the primary requirement was, understandably, a Gmail account. This was a sensible approach, leveraging Google’s massive existing user base. Furthermore, for video chat functionality, both parties involved in the call needed to have the plug-in installed. This interdependence ensured compatibility and a consistent experience across the network of users. Beyond these two fundamental prerequisites, finding “any other con” about the plug-in was genuinely challenging, a testament to its robust design and user-centric implementation.
The plug-in also played a vital role in Google’s broader social initiatives. It was the essential component required to initiate a “Google+ Hangout.” Google+, Google’s foray into social networking, heavily leveraged the video conferencing capabilities built into this plug-in to facilitate multi-person video calls, further cementing its importance in Google’s communication ecosystem. This extended utility made the plug-in even more indispensable for those deeply integrated into Google’s services.
While the “pros” overwhelmingly overshadowed the “cons,” a minor point of contention for some users was the fixed position of the embedded video window. As mentioned, if not popped out, the video chat window was static on the right side of the Gmail interface. While the “pop out” option mitigated this, some users might have preferred direct draggable manipulation of the embedded window. However, this was a small trade-off for an otherwise excellent and highly functional tool, especially considering the technical constraints of web-based applications at the time. The overall consensus was that Google had finally “added the one feature it lacked: high-quality, responsive video chats!”
The Evolution and Eventual Transition
The digital world is characterized by relentless innovation and rapid evolution. Technologies that once seemed groundbreaking quickly become standard, then obsolete, as new and improved solutions emerge. Google Voice and Video Chat, despite its initial success, was no exception to this cycle.
The Rise of Google Hangouts and Beyond
The data provided indicates that the last update for Google Voice and Video Chat was in June 2012. This timeframe coincides with a significant shift in Google’s communication strategy. As Google+ gained traction and the desire for more robust, multi-person video conferencing grew, Google began consolidating its communication efforts under a new banner: Google Hangouts. Google Hangouts was designed to be a unified communication platform, encompassing text chat, voice calls, and multi-party video conferencing, seamlessly integrating across Gmail, Google+, and eventually standalone mobile and desktop applications.
This transition meant that the standalone Google Voice and Video Chat plug-in eventually became redundant. Users were encouraged to migrate to Hangouts, which offered enhanced features, improved stability, and a more future-proof architecture. The original plug-in “can no longer be downloaded,” a clear indication of its deprecation in favor of more modern solutions. The spirit of simple, integrated video communication, however, lived on through Hangouts.
The evolution didn’t stop there. As Google further refined its offerings, Hangouts itself began to bifurcate into Google Chat (for team messaging) and Google Meet (for enterprise-grade video conferencing). This reflects a broader industry trend towards specialized communication tools tailored for specific use cases – casual social interaction versus formal business collaboration. Each iteration built upon the lessons learned from its predecessors, including the foundational principles established by the early Voice and Video Chat plug-in, particularly regarding quality, ease of use, and integration.
Reflecting on its Impact and User Reception
Despite its eventual retirement, Google Voice and Video Chat left a significant mark. For many, it was their first reliable experience with integrated video communication. User reviews from the provided content, even years after its last update, reflect its positive impact. Users like Raju Kiskureviewed on July 8, 2017, expressed satisfaction and a desire to still use it, highlighting its lasting positive impression. Other anonymous users praised its ability to help them “chat with my friends and my family” and “to call people sometimes when I lose my cell phone.” The sentiment was overwhelmingly positive regarding its primary function: connecting people.
The ease of setup and use was a recurring theme in user feedback. Even those who encountered difficulties downloading the software (a common issue with older software links and evolving web standards) recognized its inherent value and the promise of effortless connection. This underscores that while the underlying technology changes, the core human desire for simple, high-quality communication remains constant. Google Voice and Video Chat fulfilled that desire admirably during its active years, paving the way for the sophisticated communication platforms we use today.
The Broader Landscape of Communication Tools
The journey of Google Voice and Video Chat, from pioneering plug-in to deprecated legacy, illustrates the dynamic nature of digital communication. The space is continuously innovated, with new solutions emerging to address evolving user needs and technological advancements.
Legacy Alternatives and Modern Solutions
In its heyday, Google Voice and Video Chat competed in a growing market. Over time, a diverse array of alternatives, both free and paid, emerged or grew in prominence. The landscape included:
- Traditional IM Clients: Applications like Windows Live Messenger (MSN Messenger), Yahoo! Messenger, and AIM, which primarily focused on text chat but gradually added voice and video capabilities.
- Specialized Video Callers: Early pioneers like Skype significantly popularized voice and video calls, eventually becoming a dominant force before facing intense competition.
- Enterprise Solutions: Tools designed specifically for business collaboration, such as Cisco Webex and later Microsoft Teams and Zoom Meetings, which have become indispensable in remote work environments.
- Social Media Integrated Tools: Platforms like Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, and Telegram, which integrated voice and video calls directly into their messaging apps, leveraging their massive user bases.
The shift towards mobile devices also played a crucial role. Apps like WhatsApp, Telegram, and Apple’s FaceTime made video calling a native, effortless experience on smartphones, further pushing desktop-centric plug-ins into obsolescence. The alternatives mentioned in the original source, such as Google Chat, SnapTalk, TextNow, EyeBall Chat, Camfrog Video Chat, ooVoo, and Tango, represent this rich tapestry of communication options, each with its unique focus and feature set. Today, mainstream choices like Zoom Meetings, Microsoft Teams, Skype, WhatsApp, and Telegram dominate, offering robust features, multi-platform compatibility, and often, end-to-end encryption.
Choosing the Right Platform for Today’s Needs
With such a vast array of communication tools available, selecting the “right” one depends heavily on individual or organizational needs. Factors to consider include:
- Primary Use Case: Is it for casual family chats, professional meetings, large webinars, or team collaboration?
- Number of Participants: Does it need to support one-on-one calls, small groups, or hundreds of attendees?
- Platform Compatibility: Does it need to work across Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS, and web browsers?
- Feature Set: Are screen sharing, file sharing, recording, virtual backgrounds, and integrations with other tools important?
- Security and Privacy: What level of encryption and data privacy is required?
- Cost: Are free solutions sufficient, or is a paid subscription with advanced features necessary?
The legacy of Google Voice and Video Chat reminds us that even foundational tools eventually give way to newer, more capable ones. The continuous innovation in this sector means that users always have access to cutting-edge communication technologies, allowing for increasingly seamless and effective interactions across the globe.
Ensuring Digital Safety and Responsible Use
In the digital age, the importance of software integrity and responsible usage cannot be overstated. As a platform dedicated to providing software, PhanMemFree prioritizes the safety and security of its users, offering transparent information about the applications it hosts.
PhanMemFree’s Commitment to Software Integrity
PhanMemFree (formerly Softonic) employs rigorous security protocols to ensure that all files available on its platform are safe for download. This commitment is evidenced by its comprehensive scanning process:
- Multi-Antivirus Scanning: Files and associated URLs are scanned using “more than 50 of the world’s leading antivirus services” to detect and prevent any potential threats.
- Regular Reviews: Each new file upload undergoes checks, and existing files are periodically reviewed to update their security status.
- Status Indicators: PhanMemFree provides clear “Clean” or “Warning” statuses. A “Clean” status indicates that no possible threat has been detected, while a “Warning” suggests that flags might be “false positives” – benign programs mistakenly identified as malicious due to overly broad detection signatures.
- User Feedback Loop: A “Report Software” feature allows users to flag any issues they encounter, feeding valuable information back to PhanMemFree’s team for prompt investigation and resolution. This collaborative approach enhances the platform’s ability to maintain a malware-free catalog.
This robust system aims to provide users with confidence when downloading software, ensuring that they can access useful tools without compromising their device security. In the context of older software like Google Voice and Video Chat, while no longer available for download from its original sources, PhanMemFree’s historical data and security practices underscore a dedication to presenting accurate and safe information about software products.
Navigating Legalities and Software Downloads
Beyond security, it is crucial for users to understand and adhere to the legal frameworks governing software use. As explicitly stated by PhanMemFree.org, “Laws concerning the use of this software vary from country to country. We do not encourage or condone the use of this program if it is in violation of these laws.” This disclaimer serves as an important reminder of individual responsibility.
When downloading and using any software, users should always:
- Check Licensing Agreements: Understand the terms under which the software is provided (free, trial, open source, commercial license).
- Respect Copyrights: Ensure that the software is obtained through legitimate channels and not through unauthorized redistribution.
- Be Aware of Regional Laws: Certain software functionalities, such as recording conversations or data collection, may have specific legal implications depending on geographical location.
- Prioritize Official Sources: Always attempt to download software from official developer websites or reputable platforms like PhanMemFree that implement stringent security checks.
The story of Google Voice and Video Chat is a microcosm of the larger narrative of digital innovation. It highlights how technology evolves, how user needs drive change, and how platforms like PhanMemFree play a critical role in curating and protecting the digital tools that shape our interactions. While the original plug-in may be a relic of the past, its legacy lives on in the modern communication powerhouses that connect us all today, underscoring a continuous journey towards more efficient, higher quality, and more integrated digital interactions.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Version: “2.2.2.0”
- Latest update: “June 19, 2012”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 7”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “885.5K”
- Size: “819.17 KB”
















