IP Changer is a software utility designed to modify your computer’s network settings, primarily focusing on altering its IP address. While seemingly simple, the implications and uses of such a tool are multifaceted, ranging from troubleshooting network issues to enhancing online privacy. This comprehensive guide delves into the functionality, benefits, risks, and alternatives associated with IP Changer software.
Understanding IP Addresses and Their Importance
Before exploring IP Changer, understanding the fundamental role of IP addresses is crucial. An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. Think of it as your device’s digital address on the internet. This address allows other devices and servers to locate and communicate with your computer. There are two main versions: IPv4 (using four sets of numbers separated by periods, like 192.168.1.100) and IPv6 (using a longer, hexadecimal format).
Your IP address can reveal a considerable amount of information about your location, internet service provider (ISP), and even your network configuration. This information is often collected by websites and services you interact with, raising concerns about privacy and online tracking.
How IP Changer Works: Modifying Your Network Settings
IP Changer software facilitates the alteration of your computer’s IP address. It achieves this by modifying the network configuration settings, typically found within the operating system’s network interface settings. The software can either automatically assign a new IP address from the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server or allow you to manually input a specific IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
The process usually involves a few simple steps: selecting the desired network interface (e.g., Wi-Fi or Ethernet), choosing the IP address modification method (automatic or manual), and applying the changes. Once the changes are applied, your computer effectively adopts a new IP address, temporarily masking your original one.
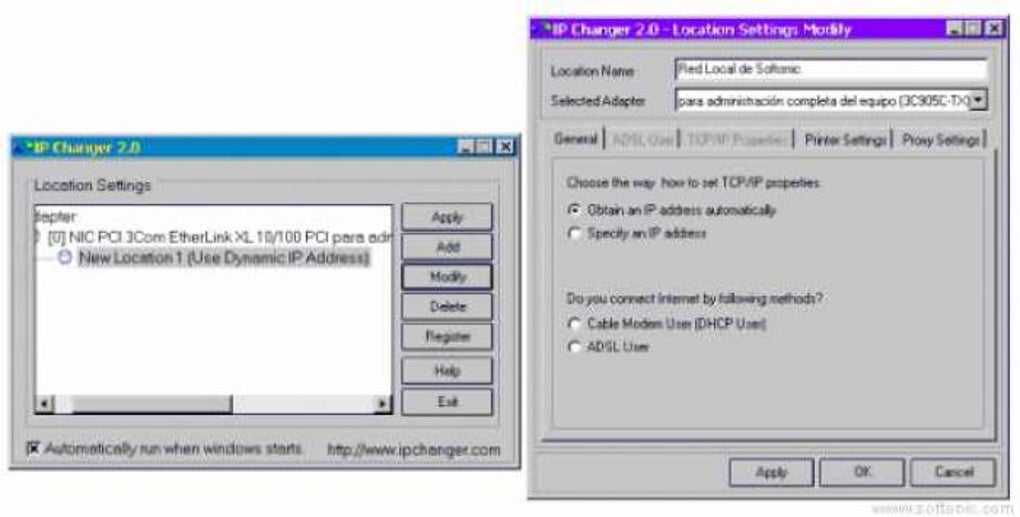
Crucially, many IP Changers offer more than just IP address modification. Advanced features might include the ability to change other network parameters like the subnet mask, default gateway, DNS (Domain Name System) servers, and even MAC address spoofing (though this is generally more complex and may not be readily supported on all operating systems). Changing DNS servers, for instance, can allow users to access content that may be blocked by their ISP or use faster, more reliable DNS servers for improved internet speeds.
Benefits of Using an IP Changer
The benefits of using IP Changer software depend heavily on the context and intended use. Here are some key applications:
-
Troubleshooting Network Issues: If your computer experiences connectivity problems, changing your IP address can sometimes resolve conflicts or glitches within your local network. A temporary IP address change can help identify whether the problem lies with your specific network configuration or a broader network issue.
-
Bypassing Geo-Restrictions: Some websites and services restrict access based on the user’s geographical location. By changing your IP address to one from a different country, you can potentially access content that would otherwise be unavailable in your region. This is often employed to access streaming services with different content libraries or circumvent regional restrictions on certain websites. However, it’s important to note that many streaming services actively work to detect and block such attempts.
-
Enhancing Online Privacy: While not a complete solution for online privacy, changing your IP address can add a layer of anonymity by masking your true location and potentially making it more difficult for websites and trackers to identify and profile you. This, however, is often best coupled with other privacy-enhancing tools like VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) or proxies for greater effectiveness.
-
Testing Network Configurations: Network administrators and developers often use IP address changes to test different network configurations and ensure their applications function correctly in various network environments. This is an essential tool for debugging and optimization in networking.
-
Accessing Specific Network Resources: In some enterprise or specialized network environments, access to certain resources might be restricted by IP address. Using an IP Changer can help a user connect to such restricted resources provided they possess the appropriate permissions.
Risks and Limitations of Using IP Changer
While IP Changer tools can be beneficial, it’s crucial to be aware of potential drawbacks and risks:
- Violation of Terms of Service: Many online services prohibit the use of IP address manipulation to circumvent geo-restrictions or access content illegally. Using an IP Changer to violate a service’s Terms of Service could lead to account suspension or even legal action.
-
Security Risks: Some unreliable IP Changer applications might contain malware or other security threats. Always download IP Changer software from reputable sources to minimize the risk of infection.
-
Temporary Solution: An IP Changer only provides a temporary solution. Your original IP address will be restored when you shut down your computer or undo the changes made by the software.
-
Network Instability: Improperly configuring your IP address can cause network instability or connectivity issues. It’s crucial to understand the network configuration settings before making any changes.
-
Detection by Websites and Services: While IP address changes can add a level of anonymity, sophisticated websites and services employ various techniques to detect and identify IP address manipulations.
Alternatives to IP Changer Software
While dedicated IP Changer software exists, other tools offer similar functionalities with added security and privacy benefits. These include:
-
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks): VPNs encrypt your internet traffic and route it through a remote server, masking your IP address and enhancing your online privacy. They offer a far more robust solution for privacy and security than simply changing your IP address.
-
Proxies: Similar to VPNs, proxies act as intermediaries between your computer and the internet, masking your IP address. However, proxies generally offer less robust security and encryption than VPNs.
-
Tor Network: The Tor network uses multiple relays to anonymize your internet traffic, making it significantly more difficult to trace your activity back to your computer. It’s significantly more private than just changing your IP but can be slower.
Choosing and Using IP Changer Responsibly
If you choose to use IP Changer software, prioritize responsible usage and safety:
-
Download from Reputable Sources: Avoid downloading IP Changer software from untrusted websites or sources. Stick to well-known software download platforms and check user reviews before installation.
-
Understand Your Network Settings: Before making any changes, understand your current network configuration settings. Incorrect configurations can lead to connectivity problems.
-
Use with Caution: Only use an IP Changer when absolutely necessary and ensure you’re not violating any terms of service.
-
Consider Alternatives: Explore alternatives like VPNs for improved privacy and security.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of IP Changer software, highlighting its functionalities, benefits, risks, and alternatives. Ultimately, the decision to use an IP Changer should be made with careful consideration of its implications and potential consequences. Remember to prioritize responsible usage and prioritize your online security and privacy.
File Information
- License: “Trial version”
- Version: “2.0”
- Latest update: “September 3, 2021”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows XP”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “44K”
- Size: “4.47 MB”
















