Mobogenie was a once-popular app management platform offering a range of services for Android and Windows users. It provided a centralized location to download applications, games, ringtones, wallpapers, and other mobile content, aiming to simplify the process of acquiring and managing digital assets on mobile devices. While no longer available for download, its impact on the mobile app landscape, particularly in regions with limited bandwidth, deserves consideration. This article explores the features, strengths, and limitations of Mobogenie, examining its place within the broader history of Android app distribution and management.
Mobogenie’s Core Functionality: A One-Stop Shop for Mobile Content
Mobogenie’s primary function was to act as an alternative app store and content management tool. Its desktop application, available for Windows, offered a user-friendly interface for browsing and downloading apps and games compatible with Android devices. The platform also provided a curated selection of ringtones, wallpapers, and other personalization options, directly catering to users’ aesthetic preferences. Beyond content delivery, Mobogenie integrated features enabling users to manage their Android devices directly from their desktop computers. This included the capability to back up and restore data, manage contacts, send and receive SMS messages, and even organize media files, all from within the Mobogenie interface.
The mobile app version of Mobogenie, though less prominently discussed now, offered a similar but more streamlined experience for direct access to apps and content on Android devices. While the desktop version served as a powerful management hub, the mobile application offered a quicker, more direct path to accessing the app store’s resources. This duality of platform support aimed to offer a holistic approach to content acquisition and device management for both casual and more tech-savvy users.
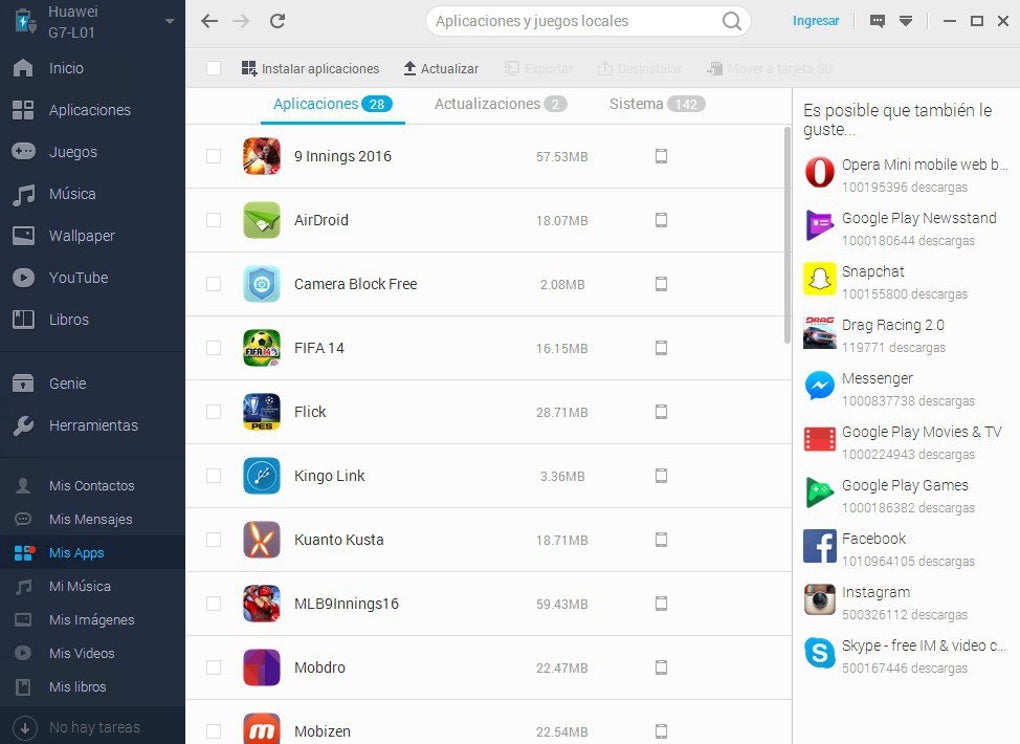
One of the critical selling points of Mobogenie was its “one-stop shop” approach. Users could access a wide range of digital resources – from applications and games to media and personalization assets – all within a single application. This was particularly beneficial in environments where multiple app stores or separate downloading processes might be cumbersome or impractical.
Personalized Recommendations and App Management Features
One of Mobogenie’s strengths lay in its personalized recommendation system. Unlike many app stores that rely solely on popularity rankings or basic categorization, Mobogenie incorporated user activity to tailor suggestions. The system analyzed user downloads and interactions to provide a more relevant selection of apps and games. This personalized approach potentially enhanced user experience by reducing the time spent searching for suitable content and increasing the likelihood of discovering potentially valuable applications that might otherwise have been overlooked.
Beyond its content delivery, Mobogenie highlighted its app management tools. The ability to back up and restore data, manage contacts from the desktop, and send SMS messages through the PC interface were significant advantages for users who desired a more comprehensive level of control over their mobile device’s functionalities. These features were particularly useful for users who preferred to manage their data efficiently via a larger screen and a keyboard, offering a more comfortable alternative to touchscreen input for certain tasks. The built-in backup functionality also provided a layer of data security, allowing users to safeguard their important information against accidental loss or device damage.
Limitations and Comparisons to Competitors
Despite its strengths, Mobogenie faced limitations. Its app library was often criticized for not matching the scale of larger app stores like Google Play Store or Amazon Appstore. While it featured many popular applications, its selection was arguably less comprehensive in terms of niche software or lesser-known applications. This limited selection could have been a deterrent for users seeking a broad range of choices or specifically searching for obscure or less mainstream apps. The curated selection, while convenient for many, might not have catered to the needs of users who preferred broader, less-filtered access to a wider range of applications.
Comparing Mobogenie to its competitors, such as Google Play Store or Amazon Appstore, revealed a clear difference in scale. Google Play Store, with its massive catalog of apps and games, and Amazon Appstore, known for its competitive pricing and extensive digital content, overshadowed Mobogenie in terms of sheer content availability. However, Mobogenie’s personalized recommendations and integrated device management features offered a degree of user experience optimization absent in the competitor platforms, attempting to address specific aspects of mobile management often overlooked by larger stores.
Mobogenie’s Target Audience and Market Niche
Mobogenie catered to a specific segment of the mobile market. Its focus on personalized recommendations and integrated device management features particularly benefited users in regions with limited bandwidth, where the efficiency of streamlined downloads and robust backup features was a crucial advantage. Countries with prevalent 2G or 3G networks, for instance, would have experienced the benefits of downloading large applications and games via a more stable home internet connection and then syncing them to their devices. This approach saved on valuable mobile data, making Mobogenie a more practical and cost-effective solution for such users. This focus on optimizing resource management highlighted a key market niche where Mobogenie offered a tangible advantage over its competitors.
Furthermore, the user-friendly interface of Mobogenie likely appealed to users less comfortable with the technical aspects of Android app management. The simplified approach to installing and updating applications, coupled with the integrated backup system, could have been particularly beneficial for users who prioritized ease of use and data security over the vast selection offered by larger app stores.
The Demise of Mobogenie and its Legacy
The reasons for Mobogenie’s eventual disappearance from the app marketplace remain somewhat ambiguous. While officially, the software’s unavailability is attributed to potential security issues or discontinuation, no precise explanation has been offered. However, its inability to keep pace with the expansion of larger app stores and the increasing sophistication of mobile operating systems might have been contributing factors. The ever-growing number of Android apps, the evolution of security standards and the rise of stricter app store regulations likely presented significant challenges for Mobogenie to overcome.
Despite its demise, Mobogenie’s legacy lies in its attempt to enhance the Android user experience, particularly in areas where mobile data and connectivity were scarce. Its focus on data management, personalized recommendations, and efficient app distribution serves as a reminder that alternative approaches can play a crucial role in enhancing user convenience and access to digital resources. The fact that it provided unique features tailored to a specific user demographic underscores that innovative strategies can always find a niche in the ever-evolving mobile technology landscape. The lessons learned from Mobogenie’s development and decline can certainly inform the development of future mobile platforms and applications. The emphasis on user-specific needs and efficient resource management may continue to be valuable considerations for app developers and platform designers in the years to come.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Latest update: “July 12, 2019”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 8”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “8.2M”
- Size: “34.80 MB”
















