Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI), the critically acclaimed action RPG from BioWare, captivated players with its expansive world, compelling narrative, and deep character customization. However, the game’s potential for enrichment is significantly amplified through the use of modifications, or “mods.” These user-created additions range from minor graphical tweaks and texture improvements to substantial gameplay alterations, adding new quests, characters, and even entire regions to explore. Managing these mods, however, can be a daunting task, especially as the number of installed modifications grows. This is where a mod manager, such as the Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI), proves invaluable.
This utility serves as a central hub for organizing and managing DAI mods, simplifying a process that could otherwise be tedious and error-prone. While several mod managers exist for DAI, this specific tool held a prominent position within the modding community for a significant period. Developed and maintained by the modding team of Eham, Zhentar, and Dawnless Sky, the Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI) streamlined the installation and management of mods, allowing players to easily enable, disable, and prioritize modifications without risking game instability.
Understanding the Need for a Mod Manager
Before diving into the specifics of the Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI), it’s crucial to understand the core issues that a mod manager addresses. Manually managing DAI mods presents several challenges:
-
Conflicting Mods: DAI mods often modify the same game files. Installing multiple mods that alter the same assets can lead to conflicts, resulting in game crashes, glitches, or unexpected behavior. A mod manager helps resolve these conflicts by prioritizing mods, ensuring that only one modification affects a particular game file. This prioritization ensures a stable gaming experience.
-
Complex Installation: Many DAI mods involve intricate installation procedures, requiring users to manually copy files into specific game directories, often with precise file renaming and placement. This manual process is prone to errors, and a single mistake can render the mod unusable or even corrupt the game files. A mod manager simplifies this process, providing a user-friendly interface for installing and uninstalling mods.
-
Organization: As the number of installed mods increases, keeping track of which mods are enabled, disabled, or conflicting becomes increasingly difficult. A mod manager provides a clear, organized view of all installed mods, allowing for easy management and control.
- Mod Dependencies: Some mods rely on other mods to function correctly, creating dependencies. Manually managing these dependencies can be cumbersome and error-prone. A mod manager automatically handles these dependencies, ensuring that required mods are installed and enabled before activating the dependent mod.
The Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI) effectively addressed these issues, offering players a much smoother and less frustrating modding experience. Its simple interface and robust functionality made it a popular choice among DAI mod users, simplifying the process of enhancing their gameplay.
Features and Functionality of the Mod Manager
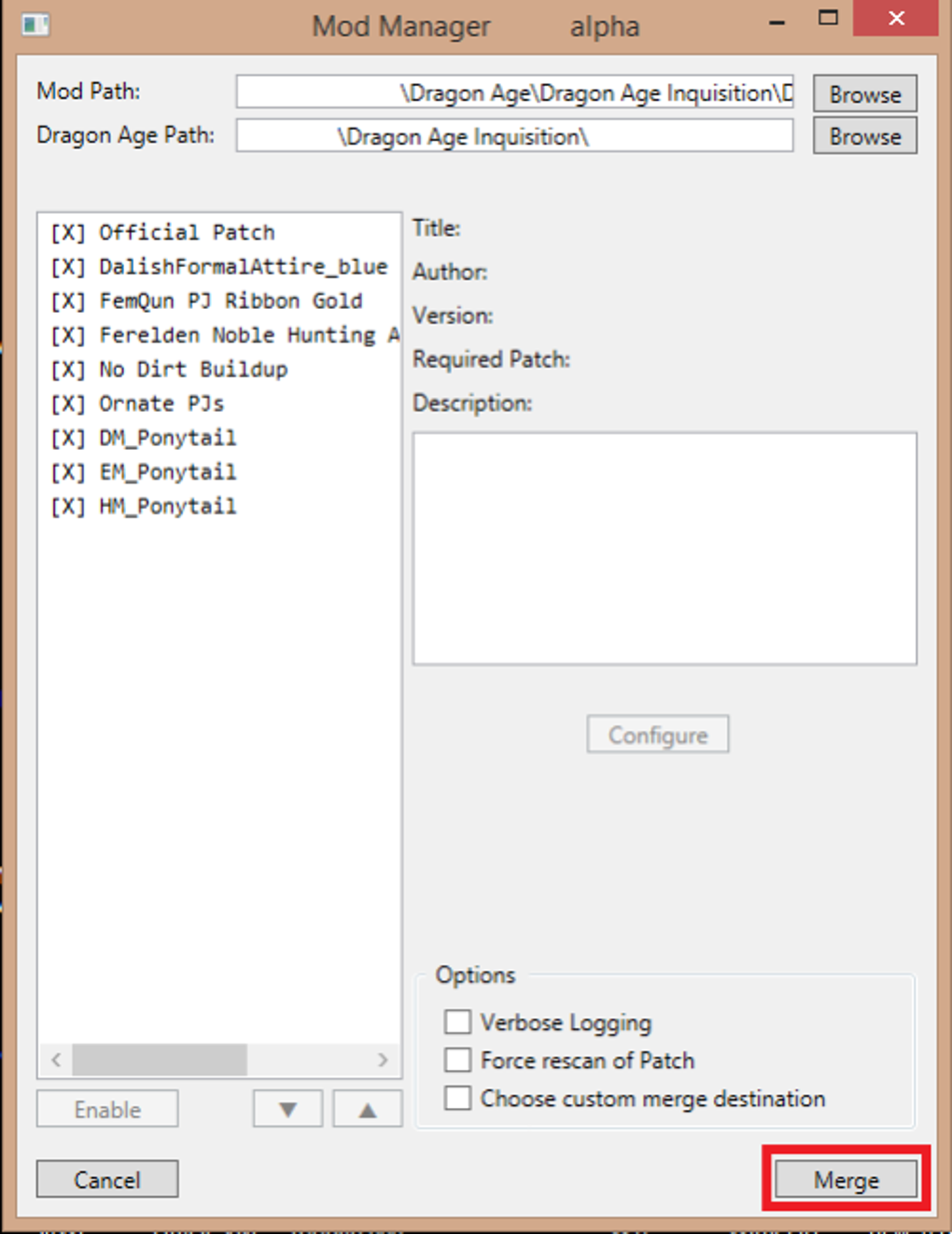
The Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI) provided several key features designed to optimize the modding experience. While not as feature-rich as some more modern mod managers, its core functionality proved highly effective for its time:
-
Simple User Interface: The manager boasted an intuitive and easy-to-use interface, making it accessible to even novice mod users. Its straightforward design allowed users to quickly navigate the list of installed mods, enabling or disabling them with a simple click.
-
Mod Prioritization: This feature was critical for managing conflicting mods. The mod manager allowed users to specify a load order, determining which mod would take precedence if multiple mods modified the same game file. This prioritization was instrumental in preventing conflicts and ensuring stability.
-
Easy Installation and Uninstallation: The manager streamlined the installation process, eliminating the need for manual file copying and renaming. Users simply selected the mod they wished to install, and the manager handled the rest. Uninstallation was equally straightforward, with the manager removing all associated files cleanly.
-
Mod Compatibility: The developers actively worked to ensure compatibility with a wide range of popular DAI mods. While not supporting every mod ever created, its compatibility with the majority of mods prevalent during its active development period was a key advantage.
-
No External Dependencies: Unlike some mod managers that require specific software or runtime environments, the Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI) operated independently, simplifying the installation process and eliminating potential conflicts with other software.
While these features made it a valuable tool, the manager’s lack of ongoing development eventually led to limitations.
Limitations and Alternatives
The primary limitation of the Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI) was its lack of ongoing maintenance. With the emergence of newer, more sophisticated mod managers and the continuous evolution of DAI mods, the original manager’s functionality began to lag. This lack of updates resulted in reduced compatibility with newer mods and a lack of support for newer features and functionalities found in contemporary mod managers. Specifically:
- Limited Compatibility with Modern Mods: As the DAI modding community progressed, newer mods often utilized updated techniques or incorporated features that the original manager couldn’t handle. This incompatibility rendered many newer mods unusable with the older manager.
-
Absence of Advanced Features: Modern mod managers frequently include features such as automated backup systems, conflict detection tools, and integrated mod download capabilities. The Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI) lacked these advanced features, placing it at a disadvantage compared to its newer counterparts.
-
No Active Support: With the cessation of development, there was no longer any active support or community troubleshooting for the Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI). This meant that users faced challenges resolving issues or finding solutions to compatibility problems independently.
Given these limitations, users seeking to mod DAI with newer mods would be better served by utilizing more modern mod managers. Popular alternatives include Frosty Mod Manager, which offers broader compatibility and more advanced features. While the Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI) served the community well during its active development, its lack of ongoing updates makes it an obsolete tool for contemporary DAI modding.
Conclusion
The Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI) played a crucial role in the DAI modding community during its active development. Its simple interface and robust functionality simplified the process of managing mods, preventing conflicts, and enhancing the overall modding experience. However, its lack of continued maintenance and updates has rendered it outdated, lacking the compatibility and advanced features found in modern mod managers. While it holds a place in DAI modding history, modern alternatives offer a significantly improved experience for today’s mod users. The legacy of the Mod Manager for Dragon Age: Inquisition (DAI) remains a testament to the dedication of its creators and their contribution to the thriving DAI modding community, highlighting the importance of community-driven development and the ongoing evolution of modding tools.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Version: “1.0.0.59-alpha”
- Latest update: “December 10, 2019”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 8.1”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “11.3K”
- Size: “142.23 KB”
















