Uber has revolutionized personal transportation, transforming how people move within cities and beyond. This ride-hailing service, accessible through a user-friendly app, connects passengers with drivers, offering a convenient and often more affordable alternative to traditional taxis and other forms of public transport. Its global reach, encompassing over 70 countries and thousands of cities, speaks to its widespread adoption and impact on the landscape of urban mobility. This article delves into the features, functionalities, and impact of Uber, exploring its evolution, advantages, and criticisms.
The Uber App: Simplicity and Convenience Redefined
The core of Uber’s success lies in its intuitive and easy-to-use mobile application. The app’s design prioritizes simplicity and efficiency, streamlining the process of requesting and managing a ride. Users simply input their desired destination, and the app, leveraging GPS technology, automatically detects their location and suggests a nearby pickup point. The app then displays a fare estimate, allowing users to make informed decisions before confirming their ride. This transparency in pricing contrasts sharply with the often-unpredictable fares of traditional taxis.
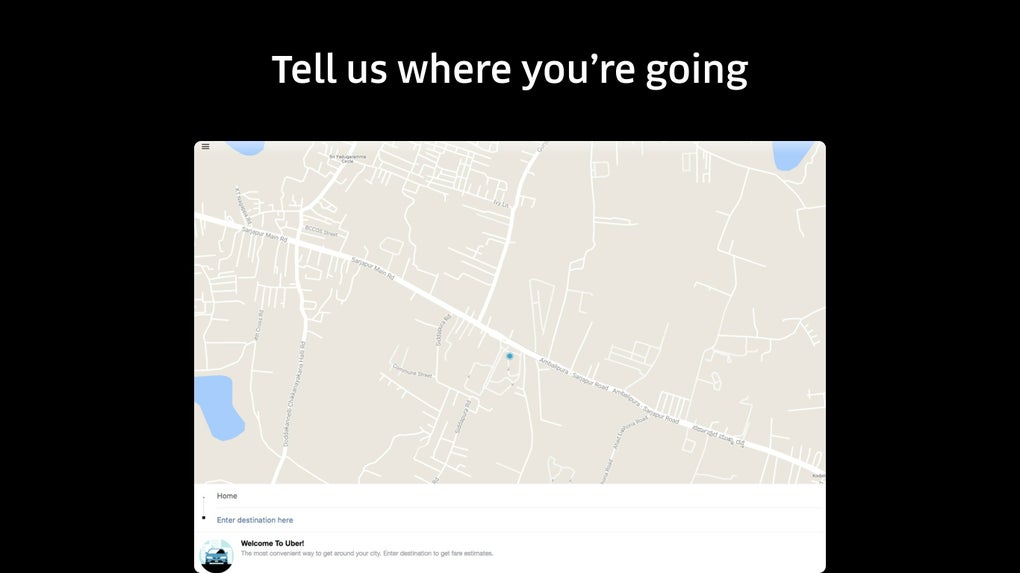
Once a ride is requested, the app provides real-time tracking of the approaching vehicle, offering peace of mind and reducing the anxiety associated with waiting for transportation. Users can view the driver’s name, photo, vehicle details, and estimated time of arrival, all within the app’s interface. This added layer of information contributes to the safety and security that are paramount concerns for many riders.
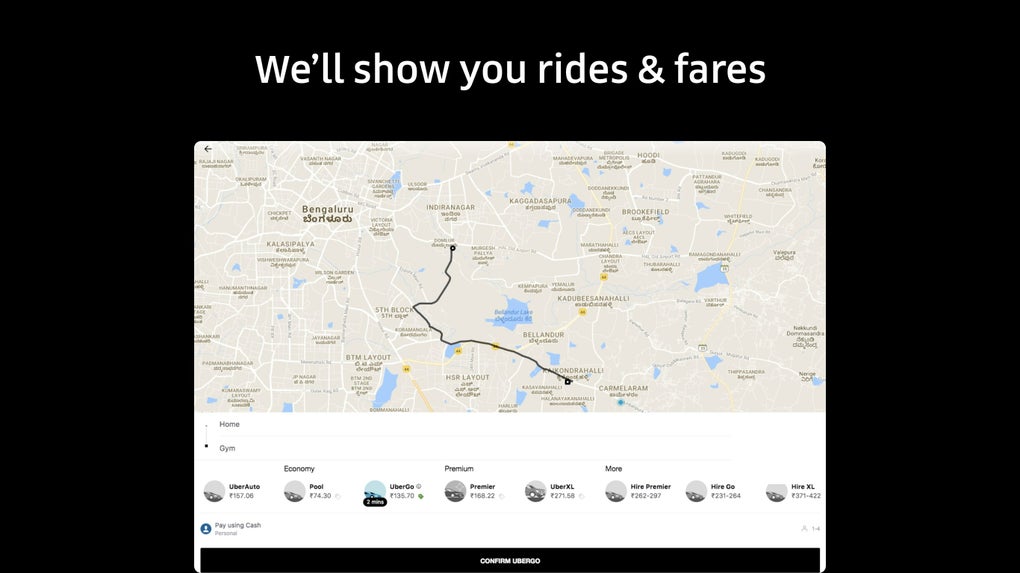
Upon completion of the ride, the app facilitates seamless payment through a variety of integrated methods. Users can choose from cash (where available), debit or credit cards, PayPal, Google Wallet, and other digital payment options. The ability to split fares with fellow passengers adds further convenience, especially for group travel. Furthermore, the app allows users to rate their experience and leave feedback for the driver, contributing to a system of accountability and continuous improvement. Conversely, drivers can also rate passengers, fostering a mutual understanding and respect within the community.
Beyond Rides: Diversification of Services
Uber’s initial focus on ride-hailing has evolved into a broader portfolio of services. The introduction of Uber Eats, for example, expanded the platform’s reach into the food delivery market, capitalizing on the existing user base and technological infrastructure. This diversification showcases Uber’s ability to adapt and meet the evolving needs of consumers, thereby consolidating its position as a leading player in the gig economy.
Beyond food delivery, Uber has explored partnerships and integrations with other service providers. This could involve collaborations with businesses offering everything from e-scooters to flower delivery, showcasing the app’s capacity to become a central hub for various on-demand services. Such expansion creates a more comprehensive platform, increasing user engagement and overall market share.
The “Saved Places” feature within the app allows users to save frequently visited locations, simplifying the ride-request process and enhancing the overall user experience. The integration of a phone number for direct contact, alongside app-based booking, provides an alternative approach for those who might prefer a more traditional method of communication.
The Uber Business Model: A Balancing Act
Uber operates on a commission-based model, receiving a percentage of each fare paid to drivers. This business model, while lucrative, has attracted criticism and legal challenges concerning worker classification and employment regulations. The debate centers on whether drivers should be classified as independent contractors or employees, with significant implications for issues such as minimum wage, benefits, and tax obligations.
The gig economy model, upon which Uber is largely built, raises complex questions about labor rights and social security. While offering flexibility and autonomy for drivers, the lack of traditional employee benefits raises concerns about income stability and worker protection. The ongoing legal battles surrounding this aspect of Uber’s business model highlight the evolving nature of work in the digital age and the need for adaptable labor laws.
Technological Innovation and User Experience
Uber’s technological advancements have played a critical role in its success. The constant updates and improvements to the app demonstrate a commitment to enhancing user experience. Features like real-time tracking, transparent pricing, and multiple payment options all contribute to a seamless and user-friendly experience.
The development of Uber Lite, a version designed for areas with limited internet connectivity, showcases Uber’s dedication to accessibility and inclusivity. This lighter version retains core functionalities, making the service available to a wider user base across diverse geographical locations and infrastructure limitations. This adaptation reflects an understanding of the global marketplace and its variations in technological accessibility.
The Future of Uber: Challenges and Opportunities
Despite its remarkable success, Uber faces ongoing challenges. Maintaining a balance between profitability and providing fair compensation for drivers remains a significant concern. Competition from other ride-hailing services and the emergence of new transportation technologies, such as autonomous vehicles, will continue to shape the future of the company. Adapting to evolving regulations and societal expectations regarding worker rights and environmental sustainability will be crucial for Uber’s long-term success.
The company’s continued investment in research and development, particularly in the area of autonomous vehicles, could represent a significant shift in its operational model and a potential solution to some of the existing challenges related to driver costs and labor relations. The potential integration of autonomous vehicles into the Uber system could represent both a significant technological leap and a substantial reconfiguration of the company’s business model.
Conclusion: Uber’s Enduring Impact
Uber’s impact on urban transportation is undeniable. Its app-based model has transformed the way people access personal transportation, offering convenience, often affordability, and a level of transparency previously lacking in the traditional taxi industry. While the company continues to navigate challenges related to labor practices, technological advancements, and intense competition, its adaptability and innovation suggest a strong position for continued growth and influence within the ever-evolving world of transportation. Uber’s journey demonstrates the power of technology to disrupt established industries and fundamentally alter everyday life. The ongoing debates surrounding its business model and its role in the gig economy will undoubtedly shape the discussion around labor regulations and the future of work for years to come.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Latest update: “November 20, 2024”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 10”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “60.2K”
- Size: “1.06 MB”
















