USB drives, while convenient for data storage and transfer, present a significant security vulnerability. Unauthorized access can lead to data breaches, identity theft, and financial losses. This comprehensive guide explores the world of USB security, focusing on software solutions, best practices, and the limitations of various approaches. We will delve into the specifics of USB Security software, examining its strengths and weaknesses.
Understanding the Need for USB Security
In today’s interconnected world, data security is paramount. USB drives, due to their portability, are particularly susceptible to theft or unauthorized access. Leaving a USB drive unattended in a public space, losing it, or having it stolen can expose sensitive personal or business information to malicious actors. This information could include confidential documents, financial data, intellectual property, personal photos, and more. The consequences of such breaches can range from minor inconvenience to severe financial and reputational damage. Strong security measures are crucial to mitigate these risks.
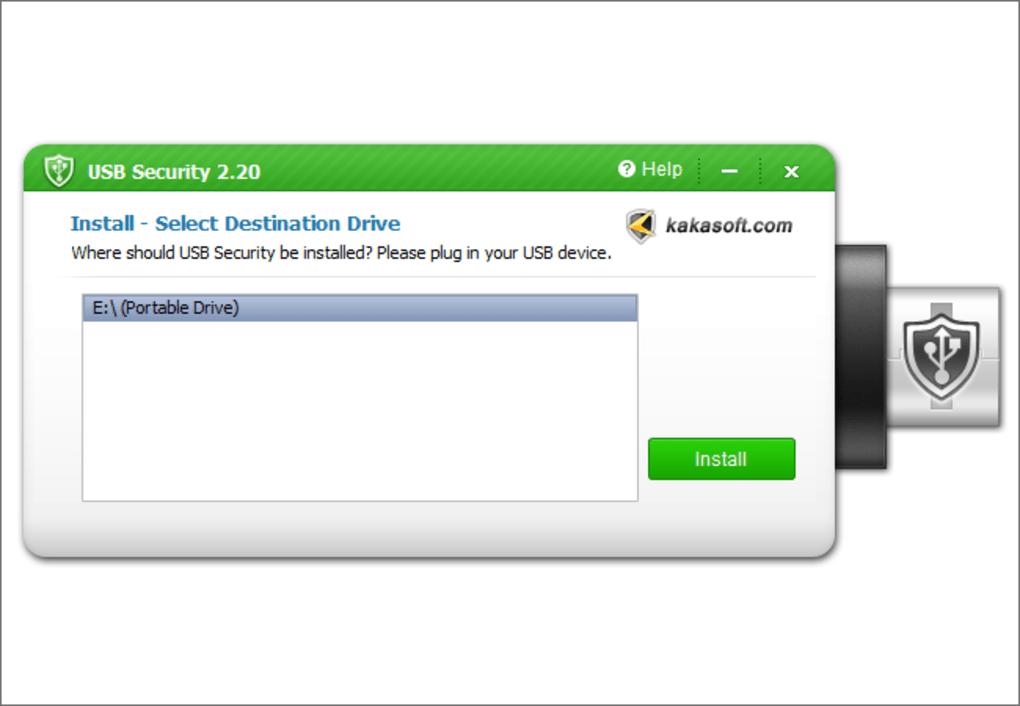
Introducing USB Security Software: A Closer Look
Numerous software applications claim to enhance USB security, offering varying levels of protection. One such application is USB Security, a free Windows-based program designed to password-protect the contents of your USB drive. While it’s simple to use, understanding its functionality and limitations is crucial before relying on it for sensitive data.
USB Security operates by creating a hidden, password-protected container on the USB drive. Upon insertion into a Windows PC, the software’s icon is visible. Accessing the underlying files requires entering the correct password. This approach differs from true encryption, which scrambles the data, making it unreadable without the decryption key.
How USB Security Works:
-
Installation and Setup: The software requires a connected USB drive for installation. During setup, the user chooses a password and an optional password hint.
-
Protection: Once the password is set, the software protects the USB drive’s content, making it invisible to the operating system. Only the USB Security icon remains visible.
-
Access: Accessing the hidden files requires launching the application and entering the correct password. The software then reveals the files, allowing the user to work with them.
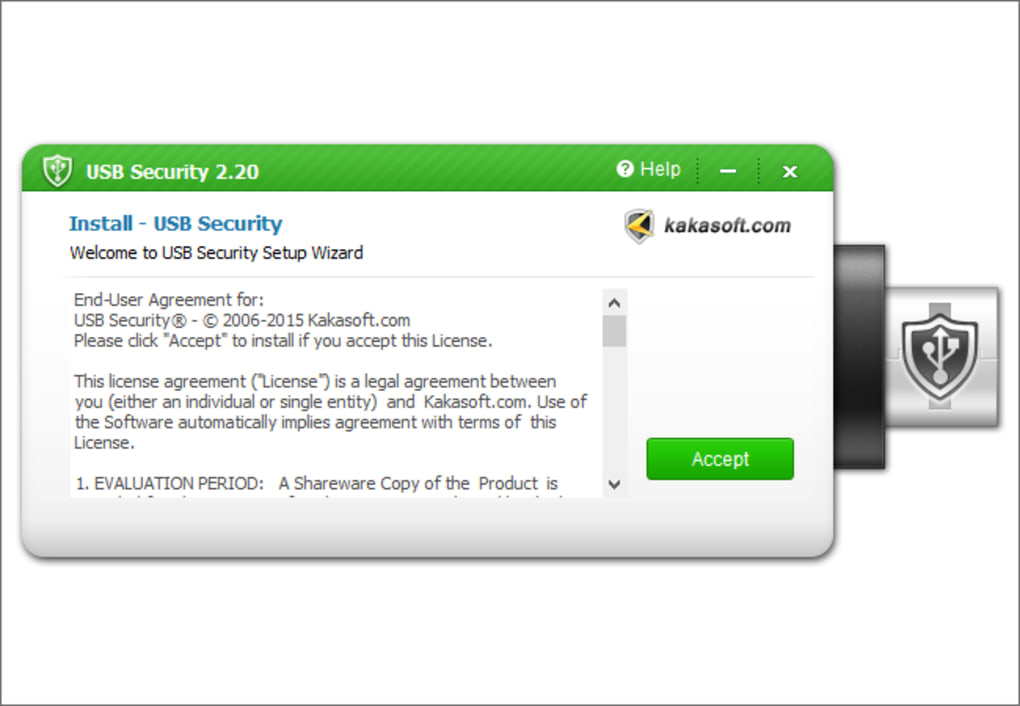
- Limitations: A crucial limitation is that the software does not automatically re-lock the drive upon ejection. The user must manually lock the drive via the application each time. This manual process is a significant security flaw and a potential point of failure. Furthermore, the software only hides data; it does not encrypt it. Sophisticated users or tools can still access the data, bypassing the software’s simple protection.
Advantages of USB Security (and similar software):
- Ease of use: The software is straightforward to install and use, making it accessible to non-technical users.
- Portability: The application resides on the USB drive itself, so it works on different computers without needing reinstallation.
- Simple protection: The password-protected container provides a basic layer of security against casual access.
Disadvantages of USB Security (and similar software):
- No encryption: The software does not encrypt data. The data remains readily accessible if the simple hiding mechanism is bypassed.
- Manual locking: The lack of automatic locking significantly weakens the security.
- Vulnerability to advanced attacks: Determined individuals with technical expertise can easily circumvent the software’s simple protection mechanisms.
- Limited platform compatibility: The software is designed for Windows only.
Alternative Approaches to USB Security
While simple software like USB Security offers a basic level of protection, more robust measures are necessary for safeguarding sensitive information. These include:
-
Full Disk Encryption: This involves encrypting the entire USB drive, making the data unreadable without the decryption key. BitLocker (Windows) and FileVault (macOS) are examples of built-in encryption tools. Third-party encryption software provides similar functionality with advanced features.
-
Hardware-Based Encryption: USB drives with built-in hardware encryption offer a higher level of security. The encryption process is handled by a dedicated chip, making it more resistant to software-based attacks.
-
Strong Passwords and Passphrases: Employing strong, unique passwords and passphrases is crucial regardless of the chosen security method. Avoid easily guessable passwords and use a password manager to generate and store secure credentials.
-
Regular Software Updates: Keep your operating system and security software updated to benefit from the latest security patches and vulnerabilities.
-
Physical Security: Physical security measures are just as important as software-based protection. Keep USB drives in a safe place, avoid leaving them unattended, and consider using a secure container or enclosure.
-
Data Backup: Regularly back up your data to a secure location, such as a cloud storage service or an external hard drive. This mitigates the risk of data loss due to theft or damage.
-
Access Control: Limit physical access to USB drives by implementing policies and procedures. This includes controlling who has access to USB ports on computers and who is permitted to use USB drives.
-
Regular Security Audits: Conduct periodic security audits to assess the effectiveness of your USB security measures. This helps identify vulnerabilities and make improvements to your security posture.
Choosing the Right USB Security Method
The choice of USB security method depends on the sensitivity of the data stored and the level of risk tolerance. For everyday use and less sensitive data, simple password protection may suffice. However, for confidential business information, financial data, or other critical data, full-disk encryption or hardware-based encryption is strongly recommended. Regardless of the method chosen, adopting a layered approach combining software, hardware, and physical security measures provides the strongest protection.
Beyond Software: Best Practices for USB Security
Effective USB security goes beyond relying solely on software. Implementing a comprehensive strategy encompassing the following practices is crucial:
-
Avoid Public Computers: Refrain from using USB drives on public or shared computers. These machines might be infected with malware that could compromise your data.
-
Scan for Malware: Regularly scan your USB drives for malware using a reputable antivirus program.
-
Use a Dedicated USB Drive: Designate specific USB drives for sensitive data to maintain a clear separation between work and personal files.
-
Remove USB Drives When Not in Use: Unplug USB drives from your computer when they are not actively being used to minimize the window of vulnerability.
-
Be Wary of Phishing and Social Engineering: Avoid clicking on suspicious links or attachments, and be cautious when receiving emails or messages asking for sensitive information.
Conclusion: A Multi-Layered Approach to USB Security
While software solutions like USB Security provide a basic level of protection, they should not be relied upon as the sole method for securing sensitive data. A multi-layered security approach combining strong passwords, full-disk encryption, hardware-based encryption (where applicable), regular malware scanning, physical security, data backups, and sound security practices is crucial to mitigating the risks associated with using USB drives. Consider the sensitivity of your data and choose a security approach that aligns with your needs and risk tolerance. Remember, data security is an ongoing process, requiring continuous vigilance and proactive measures to ensure the protection of your valuable information.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Latest update: “July 11, 2023”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 2000”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “91.3K”
- Size: “1.70 MB”
















