In the complex landscape of computer operating systems and digital storage, every component, physical or virtual, possesses a unique identifier. Among these, the “volume serial number” holds a peculiar position. Often overlooked by the average user, this identifier is crucial for certain system operations, software licensing, and even forensic analysis. Traditionally, altering this number without completely reformatting a disk volume was deemed impossible, a task often leading to data loss and significant inconvenience. This is where specialized utilities like the Volume Serial Number Editor step in, offering a precise and user-friendly solution to a historically rigid limitation. Developed by KRyLack Software, this tool empowers users to modify their disk drive’s volume serial number without the destructive process of reformatting, bridging a significant gap in standard disk management capabilities.
The digital backbone of any operating system relies on intricate identifiers to manage and distinguish between various storage devices and partitions. While a physical hard drive has its own immutable hardware serial number, each logical partition or “volume” created on that drive is assigned a distinct volume serial number, also known as a Volume ID. This identifier is automatically generated the moment a disk partition undergoes formatting. Unlike a physical serial number, which is etched into the hardware, the volume serial number is a metadata attribute of the file system itself. Its format typically appears as XXXX-XXXX, where each ‘X’ can be a hexadecimal digit (0-9, A-F), providing a vast range of unique combinations.
For years, the conventional wisdom dictated that changing this volume serial number was inextricably linked to reformatting the entire disk volume. This meant wiping all data, reinstalling the operating system, and meticulously restoring applications and personal files – an arduous and time-consuming process. This limitation posed significant challenges in specific scenarios, such as when migrating operating systems, cloning drives, or troubleshooting software that might be hard-coded to recognize a particular volume ID. The Volume Serial Number Editor emerged as a much-needed utility to circumvent this limitation, providing a non-destructive method to alter this critical identifier, thereby offering unparalleled flexibility in disk management. This comprehensive article will delve into the intricacies of volume serial numbers, explore the capabilities and practical applications of the Volume Serial Number Editor, compare it with alternative solutions, and discuss its technical specifications, ultimately providing a complete understanding of its role in modern computing.
Understanding the Essence of a Volume Serial Number
To fully appreciate the utility of a tool like the Volume Serial Number Editor, it’s essential to first grasp what a volume serial number is, how it functions, and its significance within the broader context of computer systems. A volume serial number, often referred to as a Volume ID or Disk ID, is a unique hexadecimal identifier assigned to a hard disk partition or logical volume when it is formatted. This number is not chosen by the user but rather generated automatically by the operating system during the formatting process. Its primary purpose is to uniquely identify a specific disk volume within the system, helping the operating system and applications distinguish between different drives or partitions.
The typical format of a volume serial number is a string of eight hexadecimal characters divided into two four-character segments by a hyphen, for example, C123-45AB. Each character can be any digit from 0 to 9 or a letter from A to F. This format provides a vast number of unique combinations, ensuring that the likelihood of two different volumes having the same serial number is astronomically low. It’s crucial to understand that this volume serial number is distinct from the physical serial number of the hard disk drive itself. The physical serial number is a hardware-level identifier, often printed on a sticker on the drive’s casing, and is fixed by the manufacturer. It identifies the physical hardware component, whereas the volume serial number identifies a logical partition on that component. This distinction is vital because while the Volume Serial Number Editor can change the logical volume ID, it cannot, and is not designed to, alter the physical serial number of the hard disk.
The volume serial number is stored within the metadata of the file system (NTFS, FAT, FAT32) on that particular volume. It plays a subtle but important role in how an operating system tracks and references disk volumes. For instance, some older applications, or even specific versions of software, might be hard-coded to check or rely on the volume ID for licensing purposes, installation paths, or to verify the authenticity of an original installation drive. If such an application is moved to a new drive or if the volume ID changes due to reformatting, it might cease to function or require re-activation. Similarly, in advanced scripting or batch file operations, the volume ID can be used as a stable reference point for a specific drive, regardless of its assigned drive letter which can sometimes change. Understanding this distinction and the subtle influence of the volume serial number is the first step towards appreciating the focused utility that tools like Volume Serial Number Editor bring to the table. It’s not a frequently modified attribute for most users, but for specific technical needs, its mutability without data loss is invaluable.
Unveiling the Power of Volume Serial Number Editor
The Volume Serial Number Editor from KRyLack Software directly addresses a long-standing limitation in disk management: the inability to change a disk volume’s serial number without resorting to a full reformat. This core functionality is what sets the utility apart and makes it an indispensable tool for users facing specific system configuration or software compatibility challenges. Before this tool, altering the volume ID invariably meant data destruction and hours, if not days, of system restoration. The editor eradicates this destructive requirement, offering a direct and non-invasive way to modify this critical identifier.
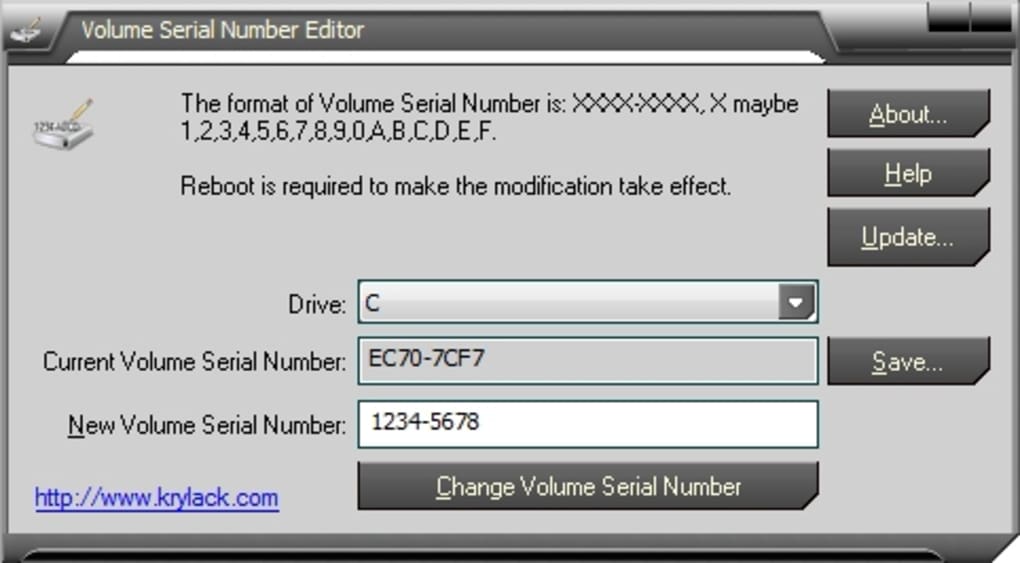
At its heart, the Volume Serial Number Editor is designed for simplicity and efficiency. It boasts a graphic user interface (GUI), ensuring that even users with limited technical expertise can navigate and utilize its features with ease. The process is straightforward: the user selects the target disk drive from a dropdown list, inputs the desired new volume serial number (Volume ID) in the XXXX-XXXX format, and then clicks the “Change Volume Serial Number” button. This intuitive workflow minimizes the potential for errors and makes an otherwise complex task accessible to a broader audience.
A significant strength of the Volume Serial Number Editor lies in its broad file system compatibility. It seamlessly supports the most prevalent file systems used in Windows environments, including NTFS, FAT, and FAT32. This comprehensive support ensures that the tool can be applied to a vast majority of disk partitions, whether they are system drives, data storage drives, or external storage devices, as long as they are formatted with one of these common file systems. This versatility makes it a go-to solution for diverse scenarios, from personal computers to more complex server setups.
Beyond its primary function, the utility incorporates a thoughtful feature for data safety and preparedness: the ability to backup the current volume serial number. Before initiating any changes, users can simply click the “Save…” button to store the existing volume ID in a text file. This simple yet crucial function provides an immediate failsafe, allowing users to revert to the original serial number if unforeseen issues arise or if the change proves unnecessary. In the realm of system modifications, the principle of backing up prior to changes is paramount, and the Volume Serial Number Editor integrates this best practice directly into its workflow.
The application is lightweight, with a modest download size of 3.74 MB for version 2.01.8, reflecting its focused functionality without unnecessary bloat. It’s a Windows-specific utility, compatible with a range of Windows operating systems, including older versions like Windows XP, making it accessible to a wide user base. With tens of thousands of downloads, it has established itself as a reliable and trusted solution for this niche but important disk management task. The Volume Serial Number Editor, therefore, stands out as a powerful, user-friendly, and safe tool for manipulating disk volume identifiers, directly addressing a problem that conventional system tools cannot solve without significant data overhead.
Practical Applications and Usage Scenarios
While the concept of changing a volume serial number might seem obscure to the everyday computer user, there are specific and practical scenarios where the Volume Serial Number Editor becomes an invaluable tool. These use cases often stem from the rigid nature of how some software and system configurations interact with disk identifiers, making the ability to modify this number without reformatting a critical advantage.
One of the most common and compelling reasons to change a volume serial number revolves around software licensing and activation. Some legacy software, or even specific enterprise applications, tie their licenses or activation mechanisms to the volume ID of the drive they are installed on. If a user upgrades their hard drive, clones their operating system to a new partition, or encounters a situation where the original volume ID changes (perhaps due to an accidental reformat of a data drive), this software might cease to function, demanding re-activation or even a complete reinstallation. By using the Volume Serial Number Editor, a user can replicate the original volume ID on the new or modified drive, effectively “tricking” the software into recognizing the new drive as the original, thereby preserving licenses and avoiding the hassle of re-activation.
Another significant application is in system cloning and disk imaging. When an operating system is cloned or an entire disk image is restored, the intent is often to create an exact replica of the original system. While most cloning software handles drive letters and file structures adeptly, the volume serial number might sometimes be regenerated on the target drive, especially if the target partition was formatted separately or if the cloning process itself assigns a new ID. For environments where consistency across multiple cloned systems is crucial, or for specific scripting that references volume IDs, ensuring identical volume serial numbers becomes important. The editor allows administrators or power users to precisely match the volume ID of a cloned drive to its source.
Batch file processing and advanced scripting represent another area where a consistent volume ID can be beneficial. While less common for the average user, system administrators or developers might create scripts that perform actions based on the volume ID of a specific drive, rather than its potentially fluctuating drive letter. If a drive’s ID needs to be adjusted to conform to an existing script or to troubleshoot a script that relies on a particular ID, the Volume Serial Number Editor provides the means to do so.
Furthermore, in some rare cases of troubleshooting and system recovery, manipulating the volume ID can be a solution. If a particular application or system component is failing to recognize a drive and diagnostic steps point to an issue with its identifier, changing the volume ID to a known good or expected value can sometimes resolve the problem. It’s a niche solution but one that can save significant time and effort in complex troubleshooting scenarios.
The usage of Volume Serial Number Editor is remarkably straightforward, thanks to its graphical user interface. Here’s a typical step-by-step process:
- Launch the application: After downloading and installing the trial version from PhanMemFree.org, launch the program.
- Select the target drive: The main interface will display a dropdown list of all detected disk volumes. Carefully select the drive whose volume serial number you wish to change. Caution is paramount here, as selecting the wrong drive can lead to unintended consequences.
- Backup the current ID (recommended): Before proceeding, click the “Save…” button to save the current volume serial number to a text file. This backup is a crucial safety measure, allowing you to easily revert if needed.
- Enter the new Volume ID: In the designated input field, type the desired new volume serial number. Remember the XXXX-XXXX hexadecimal format.
- Apply the change: Click the “Change Volume Serial Number” button. The utility will then process the request and modify the volume ID. A reboot might be required for the changes to fully take effect across the system.
While the tool is designed to be safe and non-destructive, users should always exercise caution. Ensure you have selected the correct drive, and always back up critical data before performing any system-level modifications, even if the tool claims to be non-destructive. The Volume Serial Number Editor demystifies a previously rigid system attribute, providing a targeted solution for very specific, yet critical, computing challenges.
Exploring Alternatives and Broader Disk Management Tools
While the Volume Serial Number Editor excels in its specific function of changing a disk’s volume serial number without reformatting, it’s part of a broader ecosystem of disk management and utility software. Understanding its position relative to other tools, both direct alternatives and complementary utilities, provides a more holistic view of disk manipulation capabilities available to users.
Direct alternatives that offer similar functionality are rare but do exist. One notable example mentioned in the reference content is Hard Disk Serial Number Changer. This tool, with a PhanMemFree.org rating of 3.6, also claims to change your hard drive serial number effortlessly. While its name might suggest it changes the physical serial number, it typically refers to the volume serial number, similar to KRyLack’s editor. The key differentiator between such tools often lies in their user interface, supported operating systems, specific file system compatibility, and any additional features they might offer. Both aim to solve the same core problem, allowing users to pick based on preference, interface, or specific system requirements.
Beyond direct serial number manipulation, there are other utilities that interact with or monitor various disk identifiers and health aspects:
- Virtual Serial Port Driver: This utility, though not directly related to disk volume IDs, highlights the concept of virtualizing identifiers. It allows users to create virtual COM ports, which can be useful for emulating hardware or for testing applications that require serial port communication. While different in scope, it shares the underlying principle of manipulating or simulating identifiers for system functionality.
- Hard Disk Sentinel: This is a comprehensive hard disk monitoring software. While it doesn’t change serial numbers, it provides detailed information about a hard disk’s health, performance, and temperature. It often displays various identifiers, including physical serial numbers and volume IDs, as part of its diagnostic output. Such tools are crucial for proactive disk maintenance and understanding the state of your storage devices.
- Victoria SSD/HDD: Another powerful diagnostic software, Victoria offers reliable information and diagnostic capabilities for SSDs and HDDs. It delves deep into a drive’s parameters, including low-level access and testing. Again, it’s a monitoring and diagnostic tool rather than a modification tool, but it emphasizes the importance of understanding disk characteristics.
- HDD Recovery Pro: This falls into the data recovery category, focusing on recovering information from corrupted or inaccessible storage media. While not directly related to volume IDs, it’s a critical tool for instances where data might be lost due to disk corruption or accidental reformatting – scenarios that a user might try to avoid by using a serial number changer in the first place.
It’s also worth noting the capabilities (or lack thereof) of built-in Windows tools. The vol command in Command Prompt can display the volume serial number of a drive (e.g., vol C:), but Windows does not provide a native command or GUI option to change this number without reformatting. This absence is precisely why third-party utilities like the Volume Serial Number Editor are so valuable. For command-line enthusiasts, some complex scripts might attempt to manipulate file system metadata, but these are often precarious and not officially supported, making dedicated GUI tools a safer and more reliable option.
When choosing between Volume Serial Number Editor and its alternatives, users should consider several factors:
- Ease of Use: GUI-based tools like KRyLack’s editor are generally more accessible than command-line alternatives.
- File System Support: Ensure the tool supports the specific file system of your target drive (NTFS, FAT, FAT32 are common).
- Reputation and Security: Tools from reputable developers with good reviews (like KRyLack Software) are preferable. PhanMemFree.org’s security status for the editor being “Clean” is a good indicator.
- Specific Needs: If the only requirement is to change the volume ID, a focused tool like Volume Serial Number Editor is ideal. If broader disk health monitoring or recovery is needed, then complementary tools like Hard Disk Sentinel or HDD Recovery Pro would be necessary.
In conclusion, while the Volume Serial Number Editor serves a highly specialized purpose, it fills a crucial void in disk management that is not adequately addressed by standard operating system features. Its existence alongside other powerful disk utilities underscores the diverse needs of users in maintaining, troubleshooting, and optimizing their storage devices.
Technical Specifications and Developer Insights
The effectiveness and reliability of any software utility are often reflected in its technical specifications and the reputation of its developer. The Volume Serial Number Editor by KRyLack Software is a testament to focused development, offering a compact yet powerful solution for a specific technical challenge.
Key Technical Specifications:
- License: The software is available as a Trial version, allowing users to test its functionality before committing to a purchase. This trial model is standard for many specialized utilities, enabling users to confirm compatibility and effectiveness for their specific needs.
- Version: The most recent stable version provided in the reference is 2.01.8, with a later update noted as 2.03.4(25). Regular updates typically signify ongoing maintenance, bug fixes, and potential feature enhancements, ensuring the software remains compatible with newer operating systems and addresses any discovered vulnerabilities. The latest update date of May 20, 2024, indicates active development and support.
- Platform: The Volume Serial Number Editor is specifically designed for Windows. This platform focus allows the developer to optimize the software for the Windows file system (NTFS, FAT, FAT32) and API, ensuring stable and efficient operation within that ecosystem.
- Operating System Support: It supports a range of Windows OS versions, explicitly mentioning Windows XP, which implies compatibility with subsequent versions such as Windows 7, 8, 10, and 11. This broad OS support ensures a wide user base can leverage the tool.
- Language: The primary interface language is English, making it accessible to a global audience. The availability of information about the program in other languages on PhanMemFree.org (e.g., German, Spanish, French, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Portuguese, Russian, Thai, Turkish, Vietnamese, Chinese) suggests its international reach and user interest.
- Downloads: With 15,000 downloads overall and 130 downloads in the last month (as of the reference data), the software has a consistent user base, indicating its utility and demand within its niche market.
- Size: The application is remarkably lightweight, with a download size of just 3.74 MB. This small footprint means it consumes minimal disk space and system resources, making it quick to download, install, and run even on older or less powerful machines.
Developer Insights: KRyLack Software The developer behind the Volume Serial Number Editor is KRyLack Software. While not a massive software conglomerate, developers like KRyLack Software often specialize in creating highly efficient, task-specific utilities. This focus allows them to deeply understand particular system functionalities and develop robust solutions that mainstream operating system tools might overlook. Their continued development and updates to the Volume Serial Number Editor underscore their commitment to maintaining the utility’s relevance and performance.
Security Status and User Reviews: PhanMemFree.org performs thorough security scans on all files hosted on its platform. The Volume Serial Number Editor is listed with a “Security Status” of “Clean,” meaning it’s “extremely likely that this software program is clean” after being scanned by over 50 leading antivirus services. This assurance is crucial for any utility that performs low-level system modifications, providing users with confidence in its safety.
While no specific user reviews were provided in the excerpt (it prompts users to “Be the first to leave your opinion!”), the general trend for utilities like this is that they are highly valued by the specific user base that needs them. Positive feedback typically highlights the tool’s effectiveness, ease of use, and the relief it brings by solving a previously difficult problem without data loss. Any negative feedback would usually revolve around edge cases, specific system incompatibilities, or requests for additional features.
In essence, the Volume Serial Number Editor from KRyLack Software is a well-engineered, lightweight, and secure utility that fills a specific, yet critical, gap in Windows disk management. Its technical specifications reflect a mature and maintained product, while the developer’s focus ensures a reliable solution for those who need to precisely control their disk volume identifiers. It stands as an example of how specialized software can provide immense value by addressing discrete technical challenges that mainstream tools often overlook.
File Information
- License: “Trial version”
- Latest update: “May 20, 2024”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows XP”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “15.1K”
- Size: “3.74 MB”
















