WakeMeOnLan is a free, portable remote control program for Windows PCs developed by NirSoft. It empowers users with remote access capabilities, enabling them to power on and off multiple computers simultaneously by sending Wake-on-LAN (WOL) packets. This functionality blends aspects of network management tools like Cisco Network Magic and network scanning utilities, providing a convenient solution for managing multiple machines on a local area network (LAN). Beyond its power control capabilities, WakeMeOnLan also offers basic network diagnostic features. This makes it a valuable tool for both home users with multiple PCs and IT professionals managing larger networks.
How WakeMeOnLan Works: A Step-by-Step Explanation
WakeMeOnLan’s operation is relatively straightforward, but requires a fundamental understanding of network communication and the Wake-on-LAN protocol. Upon launching the application, it initiates a network scan to identify all connected devices within the LAN. This scan gathers crucial information about each discovered computer, meticulously recording details such as its IP address, computer name, MAC address, and network adapter information and status. This data is then compiled and stored locally, creating an inventory of manageable devices. This inventory is readily accessible through the user interface, providing a clear overview of the network’s connected computers.
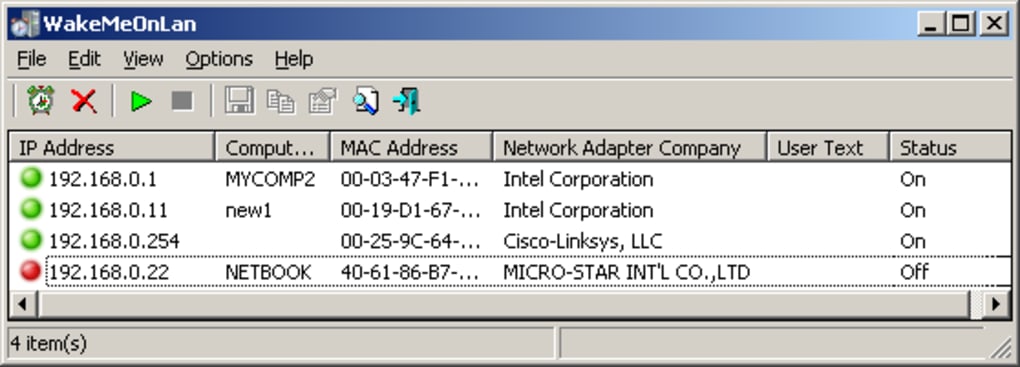
The core functionality relies on the user enabling the Wake-on-LAN feature within their network adapter properties. This enables the network card to receive and respond to the WOL packet sent by WakeMeOnLan. Crucially, depending on the system’s BIOS settings, it may also be necessary to activate Wake-on-LAN within the BIOS itself. Without this dual activation, the WOL packets sent by WakeMeOnLan might be ignored by the target machines.
Once the Wake-on-LAN functionality is properly configured, WakeMeOnLan offers three distinct methods for remotely controlling the power state of the listed computers:
-
Bulk Selection: The user interface presents a list of detected computers. Selecting multiple computers and then clicking the “Wake all selected computers” button will simultaneously send WOL packets to all selected machines, attempting to power them on. This method is efficient for managing groups of computers.
-
Right-Click Menu and Hotkey: Alternatively, right-clicking on an individual computer in the list provides a context menu offering the option to wake that specific machine. The application also supports a hotkey (F8) that triggers the same action when pressed while a computer is selected in the interface. This approach allows for targeted control of individual PCs.
- Command Line Interface: For advanced users or those integrating WakeMeOnLan into scripting environments, a command-line interface is also available. This provides precise control via specific parameters, enabling automation and integration with other system management tools. This is particularly useful in scenarios requiring programmatic control of the remote power-on function.
It’s important to note that WakeMeOnLan’s core functionalities are currently limited to wired network connections (Ethernet). Wireless (Wi-Fi) connectivity is not supported, so all target computers must be directly connected to the LAN via an Ethernet cable.
WakeMeOnLan: Strengths and Weaknesses
WakeMeOnLan, despite its age and simple interface, offers compelling advantages for managing multiple PCs on a LAN:
Advantages:
-
Speed and Efficiency: The application is lightweight and operates quickly. The network scan completes promptly, and WOL packets are sent efficiently, minimizing latency.
-
Remote Power Control: Its core strength lies in its ability to remotely power on (and, to a lesser extent, off) multiple computers simultaneously. This simplifies system management, especially for those overseeing a network of machines.
-
Network Information Gathering: Beyond remote control, WakeMeOnLan provides valuable network information, including IP addresses, computer names, and MAC addresses. This information can be instrumental in network administration and troubleshooting.
-
Free and Portable: The software is entirely free to use and doesn’t require installation. This makes it accessible to a broad range of users, and the portable nature allows for easy deployment on various machines.
Disadvantages:
-
Outdated User Interface: The user interface reflects the application’s age, exhibiting a design that feels dated by modern standards. A more modern, intuitive interface could significantly enhance usability.
-
Wired Connection Only: The limitation to wired Ethernet connections significantly restricts its use in modern networks, where wireless connectivity is prevalent.
-
Limited Functionality: While providing power control and basic network information, WakeMeOnLan lacks the extensive features found in more comprehensive network management solutions.
Alternatives to WakeMeOnLan
While WakeMeOnLan effectively addresses a specific need, alternative solutions exist that offer broader functionality or improved user interfaces:
Several commercial remote control applications provide much richer feature sets, allowing for remote desktop access, file transfer, and more advanced system management. These generally come with a cost associated with their license. Free alternatives sometimes exist, but they may have limitations similar to or even greater than those of WakeMeOnLan.
WakeMeOnLan in the Context of Network Administration
For network administrators, even with its limitations, WakeMeOnLan remains a useful tool. Its simplicity and ability to quickly power on multiple machines can streamline tasks, such as overnight batch processing or remote system maintenance. Coupled with other network management utilities, it complements broader system administration workflows. However, the limitations, particularly the outdated interface and lack of wireless support, should be considered when deciding if it fits into a larger network management strategy. For smaller, wired-only networks, it might be an ideal solution, but for larger, modern networks with a mix of wired and wireless devices, more comprehensive tools may be necessary. Its strengths remain in its simplicity, speed, and free access, making it a useful addition to a network administrator’s toolkit in appropriate contexts.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Latest update: “July 10, 2025”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 8.1”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “2.9K”
- Size: “452.94 KB”
















