Microsoft RAMMap is a powerful and free utility that provides a detailed analysis of your computer’s physical memory usage. Unlike the basic memory information offered by the Windows Task Manager, RAMMap offers a granular view of how Windows allocates and utilizes RAM, revealing insights into application memory consumption, driver memory usage, and the overall health of your system’s memory management. This comprehensive analysis allows users to identify potential memory leaks, optimize RAM usage, and troubleshoot memory-related issues. This article delves into the features, functionality, and benefits of using Microsoft RAMMap.
Understanding RAMMap’s Functionality
RAMMap operates by directly accessing and interpreting the physical memory of your system. It doesn’t rely on the high-level abstractions provided by the operating system, allowing it to present a more detailed and accurate representation of memory allocation than tools that rely on system calls. The tool’s interface is meticulously designed to present complex data in a clear and understandable format. This makes it accessible to both experienced system administrators and novice users interested in gaining a better understanding of their computer’s memory behavior.
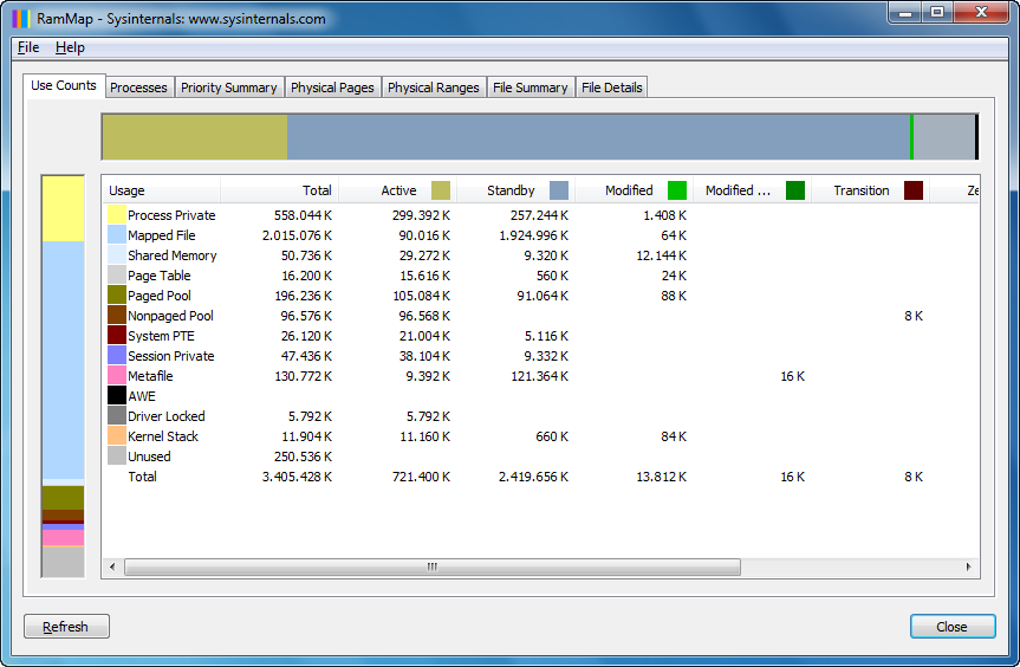
The main window of RAMMap is divided into several tabs, each providing a unique perspective on memory usage:
-
Summary: This tab provides a high-level overview of memory usage, presenting key metrics like total physical memory, available memory, and the amount of memory used by various categories like kernel code, mapped files, and private memory. This summary offers a quick snapshot of the current memory state.
-
Processes: This tab offers a detailed breakdown of memory usage by individual processes running on the system. It lists each process along with the amount of RAM it’s currently using, categorized further into various types of memory allocations. This allows users to quickly identify processes that are consuming a disproportionate amount of memory, which could be indicative of a problem or inefficient application design. The information here is significantly more comprehensive than the process memory details found in the Windows Task Manager.
-
Physical Memory: This tab provides a low-level view of physical memory usage, categorized by page state. The page states (e.g., Standby, Modified, Active, Free) describe the current status of individual memory pages. Understanding these states requires some technical expertise but offers crucial insights into memory management techniques employed by Windows. For instance, observing a large amount of memory in the “Standby” state might suggest potential areas for optimization, as this memory is currently unused but could be reclaimed.
-
Use Counts: This tab focuses on memory usage statistics, providing counts of different memory allocations. It shows the number of physical pages, virtual pages, and other memory-related metrics, offering a different perspective on memory utilization.
-
File Mapping: This is perhaps one of RAMMap’s most powerful features. This tab provides a detailed view of memory allocated to mapped files. Mapped files allow applications to access files directly in memory, speeding up operations. However, excessively large mapped files can consume considerable RAM. RAMMap shows the files currently mapped into memory, their sizes, and the processes using them. This information is incredibly useful for identifying memory bottlenecks related to file I/O operations.
Each of these tabs is color-coded for improved readability, with different colors representing different memory states or allocation types. This color-coding makes it easier to quickly identify potential issues, such as processes with high memory consumption or large amounts of unused memory.
RAMMap also includes several essential features that enhance its utility:
-
Refresh: Allows for real-time monitoring of memory changes, providing an updated view of memory usage at user-defined intervals. This dynamic display is crucial for observing memory trends and identifying memory leaks.
-
Snapshot: Provides the ability to save the current memory state to a file. This is particularly useful for comparing memory usage over time, allowing users to track changes in resource allocation after making adjustments to their system or applications.
-
Portable: RAMMap doesn’t require installation, making it highly portable. The program can be run directly from a USB drive or other portable storage media, offering flexibility and convenience.
Benefits of Using Microsoft RAMMap
The benefits of using Microsoft RAMMap extend to a wide range of users, from casual computer users to experienced system administrators. Here are some key advantages:
-
Detailed Memory Analysis: RAMMap offers a level of detail far exceeding that of the standard Windows Task Manager. It provides a deep understanding of how memory is allocated, used, and managed by the operating system and applications.
-
Troubleshooting Memory Issues: The comprehensive data provided by RAMMap is invaluable for troubleshooting memory-related problems. It helps identify memory leaks, pinpoint processes consuming excessive RAM, and diagnose other memory-related anomalies.
-
Performance Optimization: By understanding memory usage patterns, users can identify areas for optimization. This can lead to improved system performance and increased responsiveness. For example, after observing memory leaks, users can identify and resolve the underlying applications or driver issues.
-
Identifying Memory Leaks: One of the most significant benefits is the ability to identify memory leaks. Memory leaks occur when applications fail to release memory after it’s no longer needed. Over time, this can lead to a decrease in system performance or even system crashes. RAMMap can effectively pinpoint these leaks.
-
Understanding System Behavior: RAMMap provides insights into how Windows manages memory. This understanding can be beneficial for anyone seeking to enhance their knowledge of operating system internals or improve their system administration skills.
-
Ease of Use: Despite its powerful capabilities, RAMMap is relatively easy to use. The intuitive interface and color-coded displays make navigation and data interpretation straightforward, even for users without extensive technical expertise.
-
Portability: The portable nature of RAMMap eliminates the need for installation and offers convenience for troubleshooting memory issues on multiple machines.
Limitations and Considerations
While RAMMap is a valuable tool, it’s crucial to acknowledge its limitations:
- Technical Expertise Required: To fully understand and interpret the data presented by RAMMap, some technical knowledge of memory management is helpful, particularly when analyzing the “Physical Memory” and “Use Counts” tabs. The lower-level information is not always easily understandable without background in operating systems.
-
Complexity of Information: The sheer volume and detail of information presented can be overwhelming for casual users. While the interface simplifies the data, it can still present a learning curve.
-
Not a Memory Management Solution: RAMMap is a diagnostic and analysis tool, not a memory management solution itself. It identifies problems; it doesn’t directly solve them. Users must then take appropriate action to address any issues identified by the tool.
-
Interpretation Challenges: Interpreting the detailed information accurately requires a thorough understanding of Windows memory management. While the color-coding helps, misinterpreting the data could lead to inaccurate conclusions.
Alternatives to RAMMap
While RAMMap is a highly effective tool, alternative utilities provide similar, though sometimes less comprehensive, functionality. Many system monitoring tools include basic memory usage data, but rarely with the detailed breakdown available in RAMMap. These alternatives may offer simpler interfaces for less technically proficient users. However, they often lack the low-level detail and granular analysis capabilities provided by RAMMap. Therefore, the choice depends on individual needs and technical expertise.
Conclusion
Microsoft RAMMap is an indispensable tool for anyone seeking a deep understanding of their computer’s memory usage. Its detailed analysis capabilities, intuitive interface, and portable nature make it a valuable asset for troubleshooting memory issues, optimizing system performance, and gaining a comprehensive understanding of Windows memory management. While some technical knowledge is helpful for advanced analysis, the tool’s user-friendly design allows users of all skill levels to benefit from its capabilities. The information it provides is crucial for proactive system maintenance, optimization, and troubleshooting, helping ensure efficient and stable computer performance.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Latest update: “July 11, 2023”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 10”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “60.3K”
- Size: “687.33 KB”
















