Types is a free, portable Windows utility designed to manage file associations, icons, and other properties of file types within the Windows Explorer environment. While lacking comprehensive documentation and a user-friendly interface, it offers a powerful solution for users who frequently install and uninstall applications, leading to disrupted file associations. This detailed review explores its functionality, strengths, weaknesses, and provides alternatives for users seeking a simpler experience.
Understanding File Associations and Why Types Matters
In Windows, every file type (e.g., .jpg, .docx, .mp3) is associated with a specific application. When you double-click a file, Windows automatically launches the associated program to open it. However, frequent software installations and uninstalls can corrupt or overwrite these associations, leading to unexpected behavior. You might find that your preferred image viewer no longer opens JPEG files, or that your word processor fails to launch when you click a DOCX document.
Manually repairing these broken file associations can be a tedious and time-consuming process, requiring navigation through various system settings and potentially involving registry edits. This is where Types steps in. It provides a centralized interface to view, edit, and restore file associations, simplifying the process significantly. Beyond simple associations, Types also allows manipulation of icons, context menus, and other properties associated with each file type, offering a level of customization beyond the standard Windows settings.
Types’ Core Functionality: Managing File Associations and More
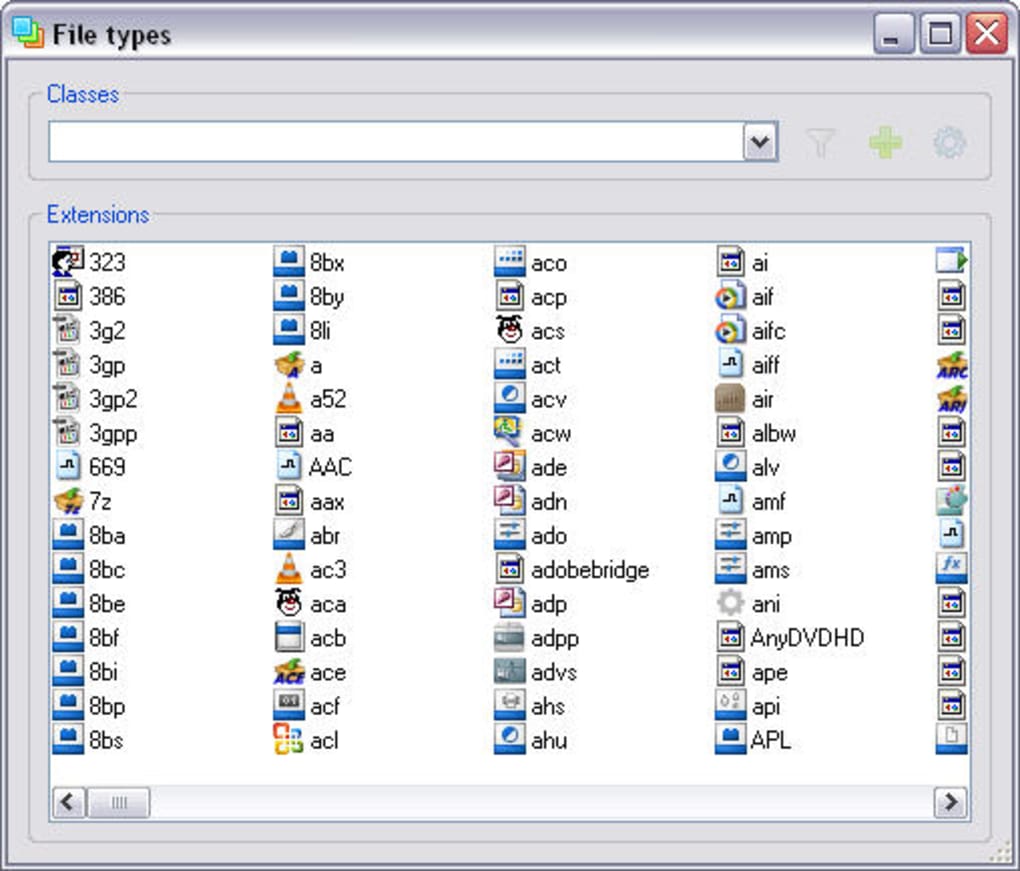
Types’ primary function is to display a comprehensive list of all file types registered on your Windows system. For each file type, it reveals the associated application, the default icon, and context menu entries. This detailed view allows users to identify problematic associations quickly.
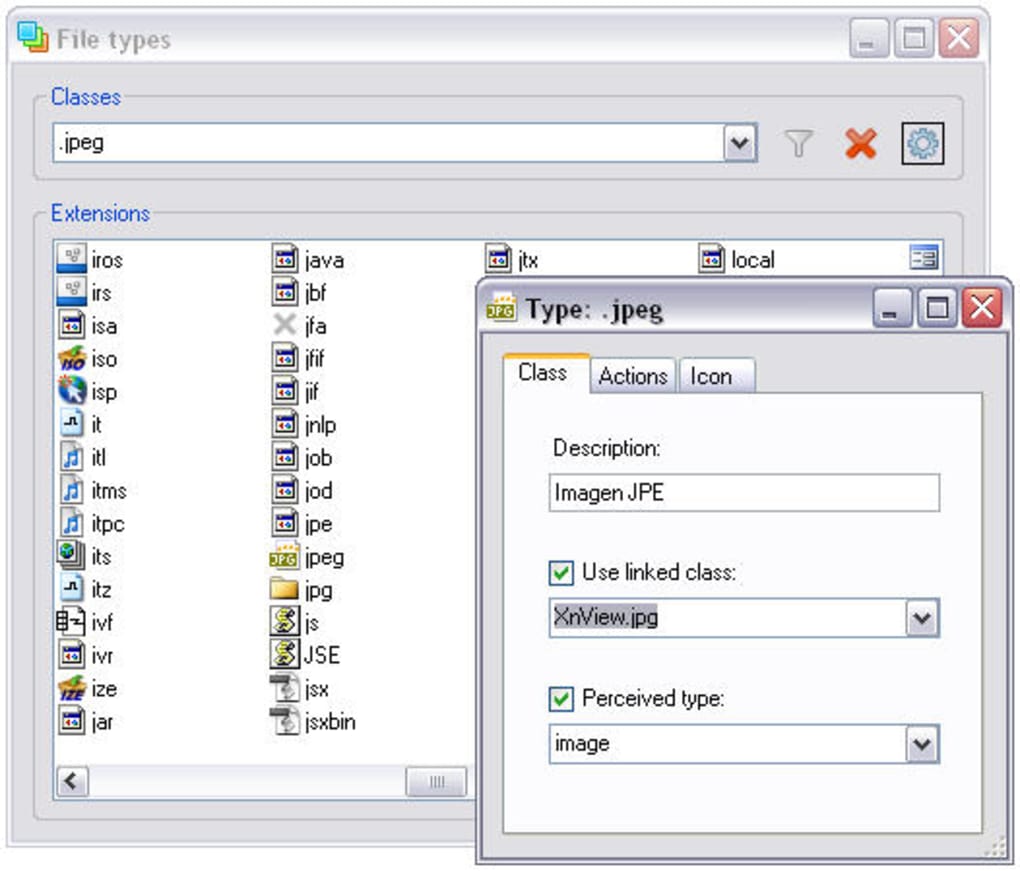
The program’s editing capabilities are where its power lies. Users can directly modify the application associated with a particular file type, effectively restoring or changing how files are opened. This allows for precise control over which program handles which file extension. For example, if a newly installed image editor has unexpectedly taken over the association for JPEG files, Types allows you to quickly revert this to your preferred viewer.
Beyond associations, Types extends its reach to other file type properties. Users can modify the icon displayed for a file type in Windows Explorer, providing a level of visual customization. The program also allows for editing context menu items, enabling the addition or removal of options that appear when you right-click a file. Finally, it provides access to other file type properties, although the exact scope of these features is not explicitly detailed within the application itself.
User Interface and Ease of Use: A Double-Edged Sword
While Types provides robust functionality, its user interface is arguably its biggest drawback. The program is text-based and lacks any visual cues or intuitive navigation. The absence of any documentation or help file further compounds this issue, making it challenging for novice users to navigate its features.
The lack of a graphical user interface (GUI) means that users need a good understanding of file types and their properties before attempting to make any modifications. Accidental changes could potentially disrupt system stability, emphasizing the need for caution and prior knowledge. While experienced users might find this level of direct control beneficial, the steep learning curve makes it unsuitable for casual users seeking a quick fix for broken file associations.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Types: A Balanced Perspective
Strengths:
- Comprehensive File Type Management: Types offers extensive control over file associations, icons, and context menu items. This level of granularity is not commonly found in other free utilities.
- Portability: The program is entirely portable, requiring no installation. This allows for easy use on multiple systems without the need for administrative privileges.
- Free and Open Source: The free license makes it accessible to all users, and its open-source nature encourages community contributions and potential improvements.
- Direct Registry Access (Implicit): While not explicitly stated, the program’s capabilities suggest it interacts directly with the Windows Registry, allowing for powerful and precise modifications.
Weaknesses:
- Steep Learning Curve: The lack of a graphical interface and accompanying documentation creates a high barrier to entry for novice users.
- Poor User Experience: The text-based interface is cumbersome and unintuitive, making navigation and modification of settings difficult.
- Risk of Accidental Damage: The powerful, low-level access to system settings carries the risk of accidental damage if modifications are not performed carefully.
- Limited Documentation and Support: The complete absence of documentation or support channels leaves users to figure out the program’s functionalities on their own. This significantly hinders adoption and usability.
Alternatives to Types: Simpler Solutions for File Association Management
For users seeking a more user-friendly alternative to Types, several programs offer similar functionality with a better user experience:
- FileTypesMan: This freeware utility provides a GUI-based interface for managing file associations and other file type properties. It offers a more intuitive approach than Types, making it easier for beginners to use.
- Default Programs Editor: Windows itself includes a built-in tool called the Default Programs Editor, accessible through the Control Panel. While not as powerful as Types or FileTypesMan, it can handle basic file association modifications.
- Third-party System Cleaners and Optimizers: Many comprehensive system maintenance tools, like CCleaner or Advanced SystemCare, include features to repair broken file associations as part of their broader functionality.
Conclusion: Types – A Powerful Tool for Experienced Users
Types remains a niche utility for users who require fine-grained control over file associations and other file-type properties in Windows. Its strengths lie in its comprehensive functionality and portability. However, the lack of a user-friendly interface and documentation severely limits its accessibility. For casual users or those seeking a simpler solution, the alternatives mentioned above offer a more intuitive and less risky approach to managing file associations. Ultimately, the choice between Types and its alternatives depends on the user’s technical expertise and the specific level of control needed. While powerful, Types’ complexity demands a cautious and knowledgeable approach to avoid potential system issues.
File Information
- License: “Free”
- Version: “2.0.6”
- Latest update: “July 12, 2019”
- Platform: “Windows”
- OS: “Windows 98 SE”
- Language: “English”
- Downloads: “7.3K”
- Size: “204.80 KB”
















